RADE
|
C++/JAVA Interactive Dashboards
|
Working with the RADE Dashboards - Part 1
Principles of use - How to Open and
Build a CAA V5 Workspace |
| Technical Article |
Abstract
This article describes the menus which appear in IBM Rational
Software Development Platform (IRAD) to provide access to CAA
V5 tools. First we will describe some principles of this customization and
then each new item.
We advise you to read the article Customizing
IBM Rational Software Development Platform [1] to set up your environment and
to migrate a CAA V5 File Tree to a format which can be used by
IRAD. If you are interested in
learning Source Code Manager functionalities, consult Working with the RADE
Dashboard & SCM [3]. If you want to develop new
CAA V5 components and to take benefits from the use of CAA V5 builders,
consult Code Generator Features [4].
Finally, if you are familiar with the CAA V5 commands, Workbench
Commands Mapping [5] will give you the
correspondences between DOS/shell commands and the dashboard menus and
windows.
|
Principles
Frameworks
and Modules vs. Workspace and Projects
IRAD uses the concepts of workspace and project.
A workspace is an area that contains projects. A project is defined as
a set of files that produces a program/library or a final binary file.
CAA V5 tools manipulate related concepts:
- In both cases the workspace represents the area where development
projects are stored. A workspace is considered as an entity with a name and a
single owner.
- IRAD projects are similar to CAA V5 Modules, since modules
are a set of files intended to produce a program (a library or an
executable).
[Top]
What Kind of
CAA V5 Commands Have Been Mapped?
The customization of IRAD includes:
- The CAA V5 Code Builder mkmk (and related tools).
- Some CAA V5 wizards: They help you create new components and files based
upon CAA V5 components.
- If some CAA V5 commands or special options are not available through the
Dashboard menus, it is possible to open a DOS window (with a proper
environment) in which all commands can be run.
[Top]
Where Are These Commands?
They are located:
- In the
File/New
wizards, under the category CAA Elements.
- In the menus
Window,
Source Code Management and
CAA Project as well as in
the contextual menu of a project in the Navigator view.
[Top]
Synchronous and
Asynchronous Commands
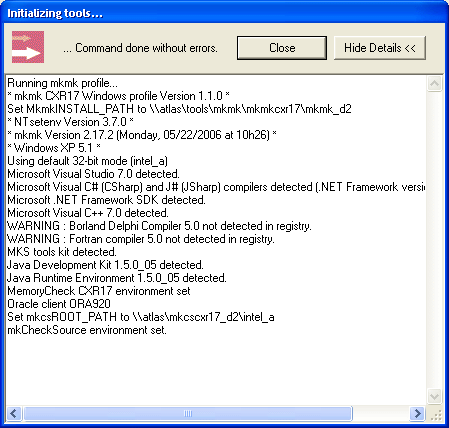
There are two kinds of CAA V5 commands:
- Synchronous commands: You must wait for their completion
to continue to work with the environment. A log window opens while a
synchronous command runs. You can swap between the
Show Details >>/Hide Details << mode of the window to browse or
hide the feedback of the command. At the end of the command, if successful,
this window disappears automatically in Hide
Details mode. If the Output is displayed, the
Break button switches to
Close. Push that button to force the
window to close. If the command fails, close the window manually.
- Asynchronous commands: These commands are launched in
the background and you can continue to work within the dashboard.
 |
For the Java Interactive Dashboard, the
output is sent to the CAA View in IRAD:
Traces are kept visible until a new command is run, allowing you to
consult these messages, especially when an informative command has been
run, in the example below we asked for the list of existing workspaces.
The traces are also saved in files in your workspace and can be
retrieved using the Window->Show
View->Other->Other->CAA View command. The lifetime of these
files is of approximately one day.
Asynchronous commands are piled in the Command Manager and executed
sequentially. The CAA Command Manager
window opens whenever an asynchronous command is running or waiting for
execution. In this window you can see commands done, running or
waiting. You can cancel a running command by selecting it in the list
and using the Stop button.
The Stop All button cancels
all commands and closes the window. When all commands have stopped, the
CAA Command Managerwindow is
closed.
CAA Output window for IRAD
 |
[Top]
What Do You Want to Do?
This section, based on a scenario, explains most of the RADE commands.
Through this scenario, you will be able to create/open/migrate a workspace,
copy an existing framework and its modules (framework CAABskDocument.edu),
build it with mkmk and execute it.
Creating a Workspace
We consider here the case where you are starting from scratch. If you
already have a workspace on your file drive, report to Customizing
IRAD [1] to
learn about how to migrate a CAAV5 File Tree to a format which can be handled
by Developer Studio.
- Activate the IRAD Customization. To do so, see
Activating IRAD
Customization.
- In the
Navigator view,
right-click a project and select New CAAV5-SCM
Workspace.
- Select the tool you want to use in the
With combo box.
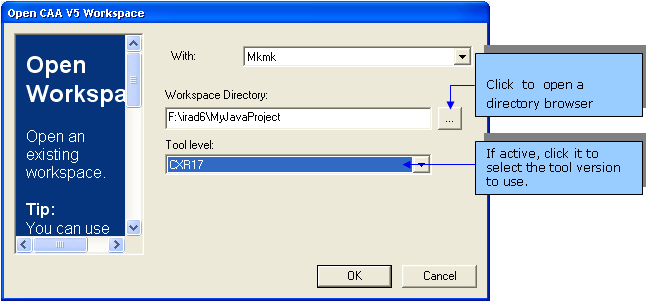
- Enter the path of the workspace root directory using a drive letter. You
can also click the
... button to
open a directory browser.
- Select the tool level in the
Tool level
combo box. If there is only one level available,
Default should be displayed in the combo box.
 |
In the New CAA V5 Workspace window,
Build On UNIX may be available
depending on how you have customized the RADE tools. To find information
on how to use the Setup tool to enable Build On Unix, refer to
Building your software
on UNIX. |
After creating the new workspace, the following window is displayed,
allowing you to create a new framework in this workspace, or to copy an
existing one. You can also cancel this step if needed.
[Top]
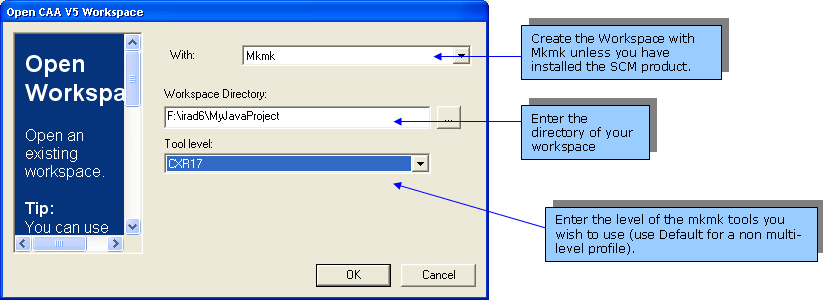
Opening a Workspace
We consider here the case where a project has been already set up, see
Customizing IBM Rational Software Development
Platform [1] to learn about how to
migrate a CAA V5 File Tree to a format which can be handled by
IRAD.
- In the
Navigator view,
right-click a project and select the Open
V5 Workspace command.
- Select the tool you want to use in the
With combo box.
- Enter the path of the workspace root directory using a drive letter. You
can also click the
... button to
open a directory browser.
- Select the mkmk level in the
Tool
level combo box. If there is only
one level available, Default should
be displayed in the combo box.
[Top]
Copy a Framework:
CAABskDocument.edu
We are going to learn how to copy a framework from a workspace to another.
We are going to copy framework CAABskDocument.edu, available in official CAA V5
education frameworks and which have been downloaded under E:\install\CAA2
directory.
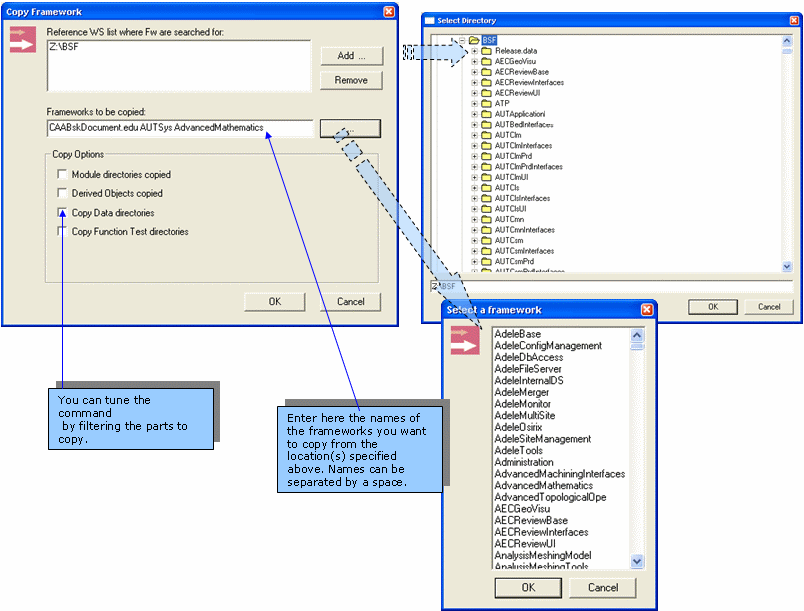
- From the
CAA Project menu,
select the Copy Framework...command.
- Enter the information required.
 |
The information you have to enter is:
- The location of the origin (where is the workspace containing the
framework to copy).
- The name of the framework to copy.
- The parts of the framework to copy: You can filter out the modules, the data directories, the derived objects (results of a build in the
origin workspace), test objects (cf.
Copy
Function Test directory), etc...
- When the origin directory is located on a Unix machine, it is not
visible from the current Window workstation. In
this case the
Add... buttons are useless and you have to enter the
usual information to allow a remote copy from the Unix machine.
|
 |
Once the copy is completed, the new framework
and module are not directly managed by the dashboards. You must update its
description files to make the new data appear. To do so, select
Update/Generate Source Folders... from
the CAA Project menu. |
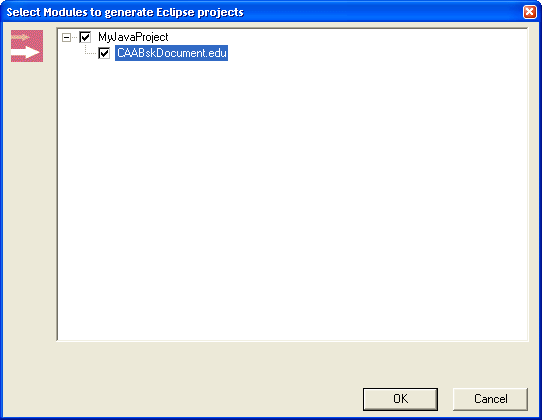
A new window is then displayed in which you can select the framework(s) and
module(s) for which a project must be generated.
For the Java Interactive Dashboard, the new frameworks and modules
are displayed in the first pane of your main window. You can generate projects
for all modules of a framework or simply for a subset of them.
If you check a framework, all corresponding modules are considered as checked.
If you just want to add some of the modules to your workspace, simply check the
modules that interest you. Note the difference between the checkmarks of a
framework when all its modules have been selected or when only a subset of its
modules have been selected. In the second case, the checkmark is partly grayed
out. This allows you to distinguish between the two cases when the file tree of
the framework has not been expanded. Be aware that whenever you generate a
project for a module, a project is necessarily generated for its containing
framework.
The generated workspace will replace the one you are currently working in,
so if you want to add some new modules or frameworks to your current workspace,
make sure that the ones already in your project are checked. In most cases,
this should already be the case. Whenever you use this functionality, your
selection is recorded and will become the default selection the next time.
[Top]
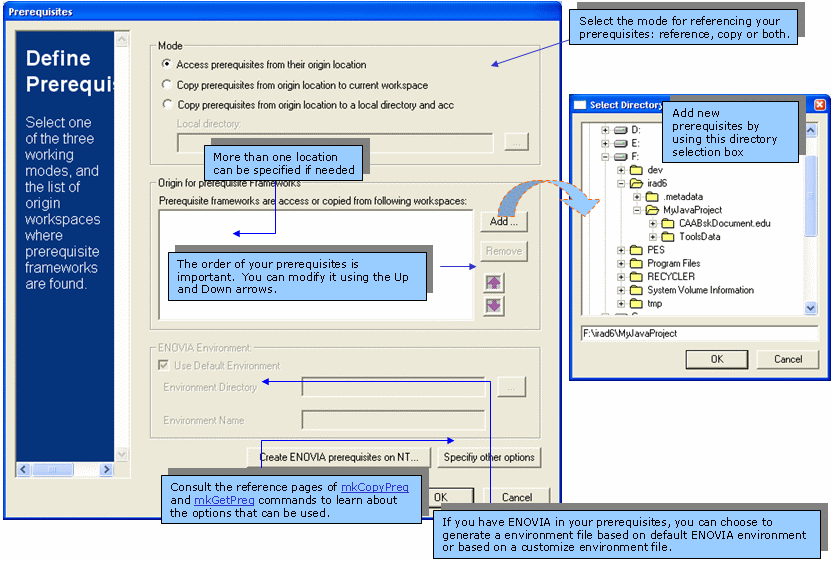
Setting up Prerequisites
The prerequisite frameworks/modules must be managed in a CAA V5 File Tree,
for instance, the directory where data have been copied from a CAA V5
build-time CD-ROM can be considered as the root of a CAA V5 workspace and can
be specified as the location of prerequisites needed by a new application.
Setting up prerequisites consists in indicating the
root
directory(ies) of workspace(s) where the code builder (mkmk) will find
necessary code to build your objects. This action can be performed several
times, the last settings replace the previous ones.
- From the
CAA Project menu,
select Get Prerequisites.... The
Prerequisites dialog box is displayed.
- Select the mode to reference your prerequisites.
 |
- The first 2 radio buttons in the mode frame give you the choice to
copy or to reference prerequisites: The choice is not so simple and we
advise you to consult the following article to find out more
information about prerequisites management: Prerequisite frameworks.
- The third mode is for more advanced users, where you can mix both
copy and concatenation modes. This is based on Build-time and Run-time
considerations and should only be used by those with a good
understanding of CATIA V5. In short, this mode performs a copy of your
buildtime prerequisites in a local directory (different from your
workspace directory), and then performs a concatenation of this
directory with other workspace(s) mandatory for runtime.
|
- Click
Add to add the
prerequisites.
- Click
OK when done.
[Top]
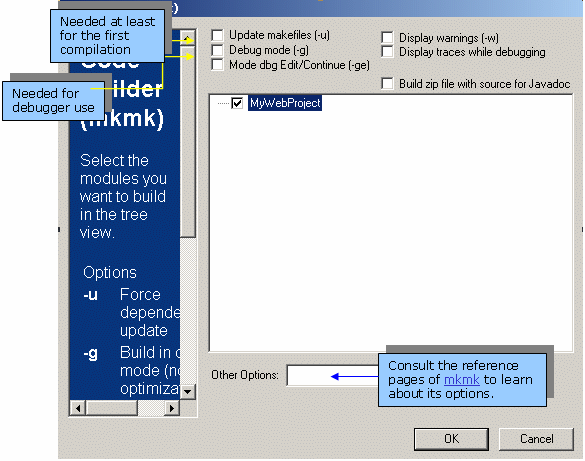
Building Your Workspace Using
mkmk
The first time you compile your program, use the mkmk builder which does not
only compile your program but also generates information that will be used
afterwards to accelerate compilations or to compile just one file.
If your program is based upon components that are not present in your
workspace (we call them prerequisites) you must first set up
your workspace by specifying the location
of these components. Then you can run mkmk.
- From the
CAA Project menu,
select mkmk.
- Check the options you require.
 |
- Update makefiles (-u) is required at least for the first
compilation.
- Debug mode (-g) is required for debugging purposes.
- Mode dbg Edit/Continue (-ge) enables you to activate the edit and
continue debug mode while compiling.
- Display warnings (-w) enables you to activate the detection of
warnings while compiling.
- Display traces while debugging enables you to Produce java source
archive files .zip while compiling.
|
[Top]
Running a Program
When you write a CAA V5 application, your application needs external
resources like dictionaries, message files, graphic resources and the like.
Those resources are delivered in data modules but scattered among many
frameworks (either your frameworks or prerequisite frameworks). So the first
thing to do before running a program is to gather resources into a common
directory that we call the Runtime View.
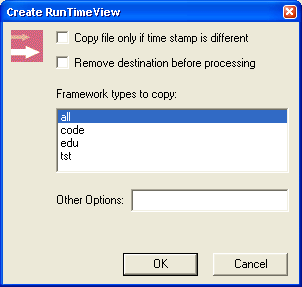
To create this Runtime View:
- From the
CAA Project menu,
select Create/Update Runtime View....
- Check
Copy file if... if
you want to reduce the amount of data to copy from the Buildtime to the
Runtime View.
- Check
Remove destination before
processing to clean up the Runtime View before
copying files.
- Select the type of the framework that you want to copy. Depending on
where you work, some kinds of frameworks may not be meaningful.
Other Options: For advanced
users (see mkCreateRuntimeView command for other options).
|
 |
In Short
- A CAA V5 workspace corresponds to an IRAD workspace.
- Frameworks and modules are mapped to IRAD projects.
- A workspace is opened by giving the path to its root directory (mkmk is
available)
- Commands are run in synchronous or asynchronous mode, 2 kinds of windows
have been defined to handle their outputs.
- The mkmk Code Builder is used instead of usual compilers, one advantage
is the support of the concatenation (prerequisite components can be searched
in other workspaces).
[Top]
References
History
| Version: 1 [Jan 2000] |
Document created |
| Version: 2 [May 2003] |
Document updated |
| Version: 3 [May 2006] |
Document updated |
| [Top] |
Copyright © 2006, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.