PPR Hub |
Product Modeler |
Enabling New Features in a Product Document to be UpdatedUpdating new features |
| Use Case | ||
| CAAPstIntegrateNewFeatures > CAAPstINFBuildCatalog > CAAPstINFCreateDocument > CAAPstINFInitCont > CAAPstINFNavigate > CAAPstINFVisu > CAAPstINFGraphicalProperties > CAAPstINFEdit > CAAPstINFCCP > CAAPstINFDelete > CAAPstINFUpdate | ||
bstractThis article discusses the CAAPstINFUpdate use case. This use case explains how to impacted features can be updated when one of their dependent features has been modified. |
This use case is intended to illustrate how to program the update of features whose definition has been modified. This occurs whenever a "CAAPstINFPoint" feature has been modified and it is referenced by a "CAAPstINFLine" or "CAAPstINFWire" feature. The referencing feature must, therefore, be updated as well in order to reflect the modification of its definition. The update itself normally consists simply in redrawing the line or wire in order to visually reflect the change in its geometry.
For features created "from scratch", two different programming tasks are necessary for a proper update to occur:
The update process works as follows:
Update method of CATISpecObject is called on the
Product document's root object in order to update the entire Product
structure. Starting with the root, each object inquires of its children
whether they are updated or not.Update method of CATISpecObject
is called in order to update the visualization of this feature.Update method of CATISpecObject calls the
CATIBuild implementation on the respective feature in order to send
a notification to the visualization process in order to visually update the
feature.You should already be familiar with the CAAPstIntegrateNewFeatures use case article [1] in order to more easily understand the context of this particular use case. A general pre-requisite knowledge of the Feature Modeler, of Providers and of the Build/Update mechanism may be required to fully understand this sample. You may want to review the basics of the Feature Modeler by looking over the "Feature Modeler Overview" technical article [2], the "Using the Provider Mechanism" use case [3] which describes the basics of the Provider mechanism and the "Build/Update Mechanism" use case [4]. Finally, it may be useful for you to look over the "Product Structure Model" technical article [5] as well.
[Top]
The CAAPstINFUpdate a use case that is part of the CAAPstIntegrateNewFeatures use case defined in the CAAProductStructure.edu framework that illustrates the integration of ObjectSpecsModeler and ProductStructure framework capabilities in the scope of a Product document.
[Top]
This use case shows how to program an Update provider in order for "from scratch" features to be taken into account during the Update process of a Product structure.
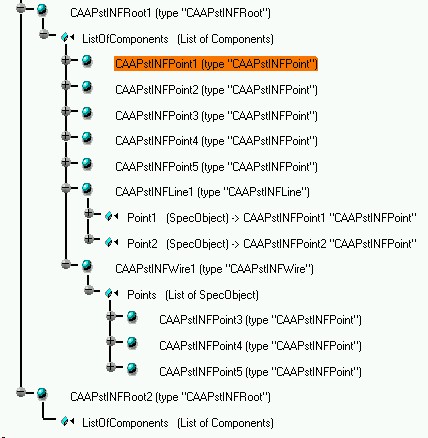
First of all, let's take a look at the contents of the Product document:
Fig. 1: Contents of the CAAPstINFDocument.CATProduct document.
 |
The "CAAPstINFLine" feature references two "CAAPstINFPoint" features. If the coordinates of any of these two points were modified, the "CAAPstINFLine" feature's geometry must be updated. Similarly, the "CAAPstINFWire" feature references a list of "CAAPstINFPoint" features so its geometry would need to be updated as well in the case the coordinates of any of the referenced "CAAPstINFPoint" features were modified.
How does this update occur?
Whenever a "CAAPstINFPoint" is modified, knowing that it is a "from scratch" feature potentially referenced by other "from scratch" features, the Update of the Product document's root is called. From there, the entire Product structure is updated, the Update providers are called, the CATIBuild implementations are executed and the impacted "CAAPstINFLine" or "CAAPstINFWire" features' visualizations are refreshed.
Let's take a look at an example by double-clicking on the "CAAPstINFPoint1" feature in order to edit it:
Fig. 2: Editing a "CAAPstINFPoint" feature.
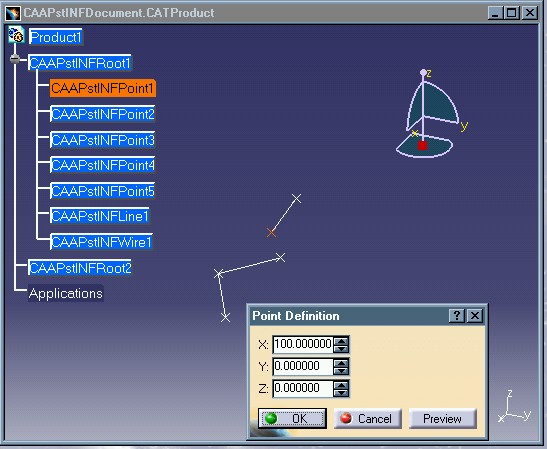 |
The dialog box entitled "Point Definition" contains the values of the coordinates of the selected point. Initially, these values were all set to 0.0. The Y coordinate value is changed to 100.0 in the dialog box and when selecting the OK button, the following modification occurs:
Fig. 3: Result of "CAAPstINFPoint" feature modification.
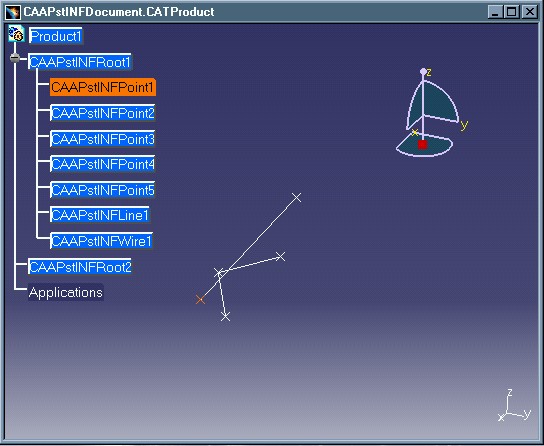 |
As you can see, the position of the point has changed and the impacted line has been re-drawn to reflect the referenced point's modification. This use case will show you in detail how the different update tasks must be programmed.
[Top]
See the section entitled "How to Launch the CAAPstIntegrateNewFeatures Use Case" in the "Integrating New Features in a Product Structure" use case for a detailed description of how this use case should be launched.
Specifically, the code described in this article is executed during the following scenario:
Launch CATIA. When the application is ready, follow the scenario described below:
CAAPstINFDocument.CATProduct in the
CAAProductStructure.edu/CNext/resources/graphic directory or select
the document you created yourself by executing the batch program described
in the previous step. The CAAPstINFDocument.CATProduct document that can be found in the CNext/resources/graphic directory of the CAAProductStructure.edu framework.
[Top]
This use case describes the implementation class of the CATIBuild interface, called CAAEPstINFBuild, which is found in the CAAEPstINFBuild.cpp source file and CAAEPstINFBuild.h header file. It also describes the implementation of the CATIUpdateProvider interface, called CAAPstINFUpdateProvider, which is found in the CAAPstINFUpdateProvider.cpp source file and CAAPstINFUpdateProvider.h header file. Both of these implementations can be found in the CAAPstINFModeler.m shared library.
| Windows | InstallRootDirectory\CAAProductStructure.edu\CAAPstINFModeler.m |
| Unix | InstallRootDirectory/CAAProductStructure.edu/CAAPstINFModeler.m |
where InstallRootDirectory is the directory where the CAA
CD-ROM is installed.
[Top]
There are three logical steps in CAAPstINFUpdate:
We will now comment each of these sections by looking at the code.
[Top]
Implementing the CATIBuild Interface for Line and Wire Features
The CATIBuild implementation of a feature is called
whenever the feature is requested to be updated by the Update
method of CATISpecObject. This particular implementation applies to
both the "CAAPstINFLine" and "CAAPstINFWire" features. The Update of these
features is called from the CATIUpdateProvider implementation
described in the next section.
HRESULT CAAEPstINFBuild::Build()
{
cout << "******* Start of: CAAEPstINFBuild::Build()" << endl;
// Retrieve a CATIModelEvents interface pointer on the current line or wire feature
// in order to send a modification notification to force its re-visualization.
CATIModelEvents * piModelEvents = NULL;
HRESULT rc = QueryInterface(IID_CATIModelEvents,
(void**)&piModelEvents);
if (SUCCEEDED(rc))
{
CATModify Notif (piModelEvents);
piModelEvents -> Dispatch(Notif);
piModelEvents -> Release();
piModelEvents = NULL;
}
else cout << "CATIModelEvents QI on Line or Wire failed." << endl;
return S_OK;
}
|
The Build method for the "CAAPstINFLine" and "CAAPstINFWire"
features consists in sending a visualization notification in order for the
geometric visualization of the features to be refreshed, taking into account
any possible modifications of the coordinates of the referenced points that
define the line or wire. The CATIModelEvents interface pointer is
first retrieved on the current feature. This means that an implementation of
CATIModelEvents must have been provided for both "CAAPstINFLine" and "CAAPstINFWire".
Then, a CATModify instance is created as well and the Dispatch
method of CATIModelEvents is executed using the CATModify
instance in order to send the notification for the visualization process to
perform the necessary refresh.
[Top]
Implementing the CATIUpdateProvider Interface
This section describes the implementation of the CATIUpdateProvider interface. This code is executed whenever an Update on the Product document's root has been requested. This occurs each time a "CAAPstINFPoint" feature's coordinates have been modified (see the "Enabling New Features in a Product Document to be Edited" use case [6]) because this type of feature is used as "input" to other features, "CAAPstINFLine" and "CAAPstINFWire". Since these features are all structured in an applicative container, it is necessary to update the entire Product structure in order to retrieve, through an Update provider, the referencing features to be updated.
Essentially, only the Update method needs to be
re-implemented. Its function is to scan the applicative container of the
current document and to update every "CAAPstINFLine" and "CAAPstINFWire"
feature contained in it.
1. Retrieve the applicative container.
int CAAPstINFUpdateProvider::Update(CATBaseUnknown * pObj, CATIDomain_var spDomain)
{
cout << "***** CAAPstINFUpdateProvider::Update" << endl << flush;
int retnum = 1;
// Retrieve a pointer to the applicative container.
CATILinkableObject *piLinkableOnObj = NULL;
HRESULT rc = pObj -> QueryInterface (IID_CATILinkableObject,
(void**) &piLinkableOnObj);
if (FAILED(rc)) return retnum;
CATDocument* pDoc = piLinkableOnObj -> GetDocument();
piLinkableOnObj -> Release();
piLinkableOnObj = NULL;
CATUnicodeString appliContIdentifier("PstINFContainer");
CATBaseUnknown *pApplicativeContainer = NULL;
rc = ::CATGetApplicativeContainer (&pApplicativeContainer,
pDoc,
IID_CATIContainer,
appliContIdentifier);
if (SUCCEEDED(rc)) cout << "Applicative container retrieved OK" << endl << flush;
else
{
cout << "ERROR in retrieving applicative container" << endl << flush;
return retnum;
}
...
|
In order to retrieve the applicative container, a CATDocument
pointer to the current document is necessary. This pointer is retrieved
through the GetDocument method of CATILinkableObject on
the calling object. Then, using the CATDocument pointer, the
applicative container called "PstINFContainer" is retrieved using the
CATGetApplicativeContainer global function of the ObjectModelerBase
framework.
[Top]
2. Retrieve a list of the features contained in the applicative container.
...
// Retrieve a pointer to CATIClientContainer in order to list the members
// of the applicative container.
CATIClientContainer *piClientOnAppliCont = NULL;
rc = pApplicativeContainer -> QueryInterface(IID_CATIClientContainer,
(void**) &piClientOnAppliCont);
pApplicativeContainer -> Release();
pApplicativeContainer = NULL;
if (NULL == piClientOnAppliCont)
{
cout << "ERROR in retrieving container pointer" << endl << flush;
return retnum;
}
else cout << "CATIClientContainer pointer retrieved OK" << endl << flush;
// Retrieve the list of features in the applicative container
CATUnicodeString clientId("CAAPstINFClientId");
CATListPtrCATBaseUnknown *pMemberList = NULL;
rc = piClientOnAppliCont -> ListMembers(IID_CATISpecObject,
clientId,
&pMemberList);
piClientOnAppliCont -> Release();
piClientOnAppliCont = NULL;
if (SUCCEEDED(rc)) cout << "Member list retrieved OK" << endl << flush;
else
{
cout << "ERROR in retrieving member list" << endl << flush;
return retnum;
}
cout << "Number of members in applicative container: " << pMemberList->Size() << endl << flush;
...
|
The list of features contained in an applicative container
can be retrieved through the ListMembers method of
CATIClientContainer on the applicative container. This method requires as
input the client id which is defined at the creation of the feature catalog
in which the StartUps of the features contained in the applicative container
have been defined. Be careful also to release each CATISpecObject
feature retrieved in the list.
[Top]
3. Update the "CAAPstINFLine" and "CAAPstINFWire" features.
...
CATUnicodeString type;
CATISpecObject *piSpecsMember = NULL;
for(int i=1;i<=pMemberList->Size();i++)
{
piSpecsMember = (CATISpecObject*) ((*pMemberList)[i]);
type = piSpecsMember -> GetType();
cout << "Type of object " << i << " = " << type.ConvertToChar() << endl;
if ((type == "CAAPstINFLine") || (type == "CAAPstINFWire"))
{
cout << "Call update on line or wire." << endl;
piSpecsMember -> Update();
}
(*pMemberList)[i] -> Release();
(*pMemberList)[i] = NULL;
piSpecsMember = NULL;
}
delete pMemberList;
pMemberList = NULL;
return 0;
}
...
|
The list retrieved from the ListMembers method
is scanned and for each "CAAPstINFLine" or "CAAPstINFWire" feature retrieved
(verified by using the GetType method of CATISpecObject),
the CATISpecObject::Update method is executed on it. This
method will call the CATIBuild implementation on the feature in order
to refresh the visualization of the feature.
[Top]
The CAAPstINFUpdate use case has shown you how program the update of a "from scratch" feature by implementing the CATIBuild and CATIUpdateProvider implementations in order for a feature whose references have been modified to be taken into account in the update process of the Product structure.
[Top]
| [1] | Integrating New Features in a Product Document |
| [2] | Feature Modeler Overview |
| [3] | Using the Provider Mechanism |
| [4] | The Build/Update Mechanism |
| [5] | The Product Structure Model |
| [6] | Enabling New Features in a Product Document to be Edited |
| [Top] | |
| Version: 1 [June 2002] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2002, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.