
3D PLM PPR Hub Open Gateway |
Feature Modeler |
Working with Feature ExtensionsExtending base features with feature extensions |
| Use Case | ||
AbstractThis article discusses the CAAOsmManageExtensions use case. This use case explains how to create extensions within a document in order to extend a base feature's behavior and data. |
This use case is intended to help you understand how to work with feature extensions in a Part or Product document. You will learn to:
Before getting to the use case itself, you should have a good understanding of the feature modeler [1]. You should likewise be familiar with the basic concepts behind feature extensions [2].
[Top]
CAAOsmManageExtensions is a use case of the CAAObjectSpecsModeler.edu framework that illustrates ObjectSpecsModeler framework capabilities.
[Top]
The goal of CAAOsmManageExtensions is to illustrate working with feature extensions. It uses the extensions created in catalogs by the CAAOsmCreateExtensions use case [3]. It also uses the base feature "CAAOsmNovel" instantiated from the catalog created in the CAAOsmCatalogSU use case [4]. These two use cases are, therefore, pre-requisites to this one.
Here is an image of the "CAAOsmNovel" StartUp:
 |
This use case calls one global function: CAAOsmIllustrateExtensions
creates a new Part document in which a new applicative container is created
to contain an instance of the "CAAOsmNovel" StartUp:
 |
Two other applicative containers are then created, the first of which contains two extensions to the "CAAOsmNovel1" base feature:
 |
 |
The second contains one other extension to the "CAAOsmNovel1" base feature:
Once these two applicative containers have been created, the use case illustrates how to extend the base feature by adding extensions within these two applicative containers. Here is a view of the inter-relationships between the catalogs and the applicative containers as well as the created extension of the base feature:
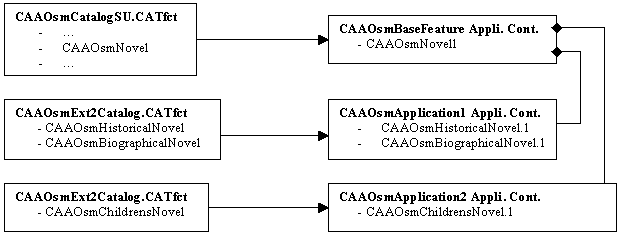 |
These data and behavior extensions are coherent with the declaration in the CATRsc files associated with the three extension StartUps[3].
CAAOsmNovel feature is extendable with the
CAAOsmHistoricalNovel, CAAOsmBiographicalNovel and
CAAOsmHChildrensNovel extensionsCAAOsmApplication1 applicative container only contains
instances of the CAAOsmHistoricalNovel and
CAAOsmBiographicalNovel CAAOsmApplication2 applicative container only contains
instance of the CAAOsmHChildrensNovel Here are the contents of the three CATRsc files:
| ExtensionFeature.IsLocal="TRUE"; ExtensionFeature.Extends="CAAOsmNovel"; ExtensionFeature.Container="CAAOsmApplication1"; |
| ExtensionFeature.IsLocal="TRUE"; ExtensionFeature.Extends="CAAOsmNovel"; ExtensionFeature.Container="CAAOsmApplication1"; |
| ExtensionFeature.IsLocal="TRUE"; ExtensionFeature.Extends="CAAOsmNovel"; ExtensionFeature.Container="CAAOsmApplication2"; |
Once the base feature is extended, the use case shows how to modify the
data of an extension by using an interface implemented on one of the three
extension StartUp. For the use case, the CAAIBiogNovel interface has
been created, and implemented on the CAAOsmBiographicalNovel
StartUp.
Finally, the use case removes extensions on the CAAOsmNovel instance.
[Top]
To launch CAAOsmManageExtensions, you will need to set up the build time environment, then compile CAAOsmManageExtensions along with its prerequisites, set up the run time environment, and then execute the use case. This is fully described in the referenced article [5]. To launch the use case, execute the following command:
mkrun -c "CAAOsmMainManageExt CAAOsmExt1Catalog.CATfct
CAAOsmExt2Catalog.CATfct CAAOsmCatalogSU.CATfct DocumentStorageName
|
Where:
[Top]
The main CAAOsmManageExtensions code is located in the
CAAOsmMainManageExt.m module of the CAAObjectSpecsModeler.edu framework. It
contains a unique source file named CAAOsmMainManageExt.cpp. This main calls
one global function: CAAOsmIllustrateExtensions, contained in
the CAAOsmIllustrateExtensions.cpp source file found in the
CAAOsmManageExtensions.m module. The CAAOsmIllustrateExtensions
function also calls methods defined by the CAAIBiogNovel interface and
implemented in the CAAEOsmBiogNovel.cpp source file also found in the
CAAOsmManageExtensions.m. Here is the installation path, depending on the
operating system:
| Windows | InstallRootDirectory\CAAObjectSpecsModeler.edu\CAAOsmMainManageExt.m
and CAAOsmManageExtensions.m |
| Unix | InstallRootDirectory/CAAObjectSpecsModeler.edu/CAAOsmMainManageExt.m
and CAAOsmManageExtensions.m |
where InstallRootDirectory is the root directory of your CAA
V5 installation.
[Top]
There are twelve logical steps in CAAOsmManageExtensions:
We will now comment each of these sections by looking at the code. This
code is found in the CAAOsmIllustrateExtensions global function
called by the main program.
CATDocument *pDoc = NULL;
rc = CATDocumentServices::New("Part",
pDoc);
...
|
A new Part document is created using the New method of
CATDocumentServices. This is the document that will contain the
applicative containers in which the base feature's extensions will be created.
[Top]
...
CATIdent idAppliCont = "CATFeatCont";
CATUnicodeString appliContIdentifier("CAAOsmBaseFeature");
CATBaseUnknown *pBaseFeatureAppliCont = NULL;
rc = ::CATCreateApplicativeContainer(&pBaseFeatureAppliCont, // appli cont created
pDoc, // document
idAppliCont, // type of appli cont
IID_CATIContainer, // interface type of appli cont
"", // supertype of appli cont
appliContIdentifier); // name of appli cont
...
CATIContainer *piBaseFeatureAppliCont = (CATIContainer*) pBaseFeatureAppliCont;
|
To create a new applicative container, use the
CATCreateApplicativeContainer global function. This function takes as
arguments:
pBaseFeatureAppliCont - the pointer that references the
new applicative container that is to be created. Its type can be a
CATIContainer or a CATIClientContainer, depending on the value
of the fourth parameter.pDoc - the CATDocument pointer to the current
document in which the applicative container will be createdidAppliCont - if the value of this argument is not "CATFeatCont",
the fifth parameter, the supertype, must be "CATFeatCont".
This argument is the type of the container that will be created.IID_CATIContainer - the interface IID that this new
applicative container will implement. If a CATIClientContainer
handle were needed, this parameter would be: IID_CATIClientContainer."" - this is the supertype of the applicative
container. If left blank, the idAppliCont argument must be "CATFeatCont".
Otherwise, this argument must be "CATFeatCont" itself.appliContIdentifier - the name of this new applicative
container.Note that the new applicative container created must be of type "CATFeatCont"
or be of a type deriving from "CATFeatCont", as seen in the
fifth argument "supertype".
Finally, the CATBaseUnknown pointer to the applicative container is cast to a CATIContainer pointer in order to be used to open the catalog of StartUps.
Two other applicative containers are created in the same way as shown above. The first will have as identifier "CAAOsmApplication1" and will contain the extensions from the first extensions catalog created in the "Creating Extension" use case [3]. The second will have as identifier "CAAOsmApplication2" and will contain the extensions from the second extensions catalog created in the same "Creating Extension" use case.
See the CAAOsmAppliCont [6] use case for a more
detailed description of this service (CATCreateApplicativeContainer)
in interactive context.
[Top]
...
CATUnicodeString catalogName = pFeatureCatalogName;
CATICatalog *piStartUpsCatalog;
CATUnicodeString clientId("CAAOsmClientId");
rc = ::AccessCatalog (&catalogName,
&clientId,
piBaseFeatureAppliCont,
&piStartUpsCatalog);
...
|
To open a catalog, use the AccessCatalog global function that
takes the following arguments:
catalogName - the name of the catalog without the storage
path and with the .CATfct extension. The catalog must be found under the
"WS" + "OS" + resources + graphic directory.clientId - the client id defined on the catalog at the
time of its creation.piBaseFeatureAppliCont - a CATIContainer pointer to
the applicative container in which StartUps or extensions from the catalog
will be instantiated.piCatalog - the returned CATICatalog pointer to the
StartUps or extensions catalog that has been opened.The two extensions catalogs whose names are passed in as arguments to this function are opened in the same way as shown above.
[Top]
1. Retrieve the "CAAOsmNovel" StartUp from the StartUp catalog.
...
CATBaseUnknown *pNovelSU = NULL;
CATUnicodeString novelSUType("CAAOsmNovel");
rc = piStartUpsCatalog -> RetrieveSU(&pNovelSU,
&novelSUType,
"CATISpecObject");
...
|
2. Create a new feature by instantiating this StartUp in the first applicative container.
...
CATISpecObject *piNovelSU = (CATISpecObject*) pNovelSU;
CATISpecObject *piNovelInst1 = piNovelSU -> Instanciate(CATUnicodeString("CAAOsmNovel1"),
pBaseFeatureAppliCont);
...
|
3. Get a CATIOsmExtendable pointer on the new base feature object.
...
CATIOsmExtendable *piExtendableOnNovelInst1 = NULL;
rc = piNovelInst1 -> QueryInterface(IID_CATIOsmExtendable ,
(void**) &piExtendableOnNovelInst1);
...
|
[Top]
... const char *extensionName = "CAAOsmHistoricalNovel"; rc = piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> AddExtension (extensionName); ... extensionName = "CAAOsmBiographicalNovel"; rc = piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> AddExtension (extensionName); ... |
An extension is added to a base feature instance, thanks a
CATIOsmExtendable interface pointer. piExtendableOnNovelInst1
just retrieved in the previous section, is a CATIOsmExtendable
interface pointer on the new CAAOsmNovel instance. The
AddExtension method of the CATIOsmExtendable interface contains
only one argument: the name of the extension StartUp. This method has
two functionalities:
AccessCatalog global function. This method returns E_FAILS in at least three cases:
In this case, both extensions from the first extensions catalog are instantiated in the "CAAOsmApplication1" applicative container.
[Top]
... extensionName = "CAAOsmChildrensNovel"; rc = piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> AddExtension (extensionName); ... |
The extension from the second extensions catalog is instantiated in the
"CAAOsmApplication2" applicative container. See the CATRsc file associated
with the CAAOsmChildrensNovel feature extension in the
What Does CAAOsmManageExtensions Do section.
To verify that an extension is created, use the QueryExtension
method of CATIOsmExtendable interface.
...
CATIOsmExtension *piExtensionOnChildrensNovelInst1 = NULL;
rc = piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> QueryExtension (extensionName,
IID_CATIOsmExtension,
(void**) &piExtensionOnChildrensNovelInst1);
...
|
The QueryExtension method retrieves the unique
extension of the base feature whose the name is extensionName.
You can choose the returned handler on the extension. Here we have choosen an
interface implemented by all the feature extension, the CATIOsmExtenson
interface.
Note that now, the base feature object has been extended by three different extensions
[Top]
1. Retrieve a pointer on the feature extension .
...
CAAIBiogNovel *piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 = NULL;
char* BiographicalNovelId = "CAAOsmBiographicalNovel";
rc = piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> QueryExtension(BiographicalNovelId, IID_CAAIBiogNovel,
(void**) &piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1);
...
|
piExtendableOnNovelInst1 is a
CATIOsmExtendable interface on the new base feature - See the
Get a CATIOsmExtendable pointer on
the new base feature object sub-section of the
Creating a Base Feature in the First Applicative Container by Instantiating a
StartUp section.
2. Execute the methods of the interface which retrieve and valuate the extension's attribute values.
// Get the value of the Epoch attribute of the CAAOsmBiographicalNovel extension.
CATUnicodeString epoch("");
rc = piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 -> GetEpoch(&epoch);
cout << "Epoch = " << epoch << endl << flush;
// Set a new value to the Epoch attribute
epoch = "Renaissance";
rc = piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 -> SetEpoch(epoch);
epoch = "";
rc = piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 -> GetEpoch(&epoch);
cout << "*** New Epoch = " << epoch << endl << flush;
// Get the value of the Domain attribute of the CAAOsmBiographical Novel extension.
CATUnicodeString domain("");
rc = piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 -> GetDomain(&domain);
cout << "Domain = " << domain << endl << flush;
// Set a new value to the Domain attribute
domain = "Science";
rc = piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 -> SetDomain(domain);
domain = "";
rc = piBiogNovelOnNovelInst1 -> GetDomain(&domain);
cout << "*** New Domain = " << domain << endl << flush;
|
"Epoch" and "Domain" are attributes of the
CAAOsmBiographicalNovel extension on the current base feature,
"CAAOsmNovel1". The methods: GetEpoch, SetEpoch,
GetDomain and SetDomain are defined by the
CAAIBiogNovel interface and implemented by the CAAEOsmBiogNovel
implementation class.
[Top]
...
CATListPtrCATBaseUnknown *paExtList = NULL;
piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> QueryAllExtensions (IID_CATISpecObject, &paExtList);
CATUnicodeString pExtId = NULL;
int jj = 0;
CATIOsmExtension *piExtensionOnBase = NULL;
if (NULL != paExtList)
{
cout << "List size = " << paExtList -> Size() << endl << flush;
for (jj=1; jj<=paExtList->Size(); jj++)
{
CATBaseUnknown * pInt = (*paExtList)[jj] ;
if ( NULL != pInt )
{
rc = pInt -> QueryInterface(IID_CATIOsmExtension,
(void**) &piExtensionOnBase);
// each non nul element of the paExtList must be released
pInt -> Release();
pInt = NULL ;
...
piExtensionOnBase -> GetID(pExtId);
cout << "Extension ID = " << pExtId.ConvertToChar() << endl << flush;
piExtensionOnBase -> Release();
piExtensionOnBase = NULL;
}
}
delete paExtList;
paExtList = NULL;
...
|
The QueryAllExtensions method of CATIOsmExtendable retrieves
a list of all of the extensions (all confused applicative containers ) of a
base feature object. It takes the following arguments:
IID_CATISpecObject: this is a filter on the interface (any
interface, not just CATISpecObject as in this case) implemented by
the extension.paExtList: this is the pointer to the list of
CATBaseUknown pointers to the extensions answering this query.The list is scanned: For each CATBaseUnknown pointer in the list,
the corresponding CATIOsmExtension pointer is retrieved in order to
get the name of the extension using the GetID method. Here is
what the output looks like:
List size = 3 Extension ID = CAAOsmChildrensNovel Extension ID = CAAOsmBiographicalNovel Extension ID = CAAOsmHistoricalNovel
[Top]
appliContIdentifier = "CAAOsmApplication1"; rc = piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> RemoveApplicativeExtensions (appliContIdentifier); |
All of the extensions of a given applicative container can be removed at
once using the RemoveApplicativeExtensions global function.
[Top]
...
paExtList = NULL;
piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> QueryAllExtensions (IID_CATISpecObject,&paExtList);
piExtendableOnNovelInst1 -> Release();
piExtendableOnNovelInst1 = NULL;
if (NULL != paExtList)
{
cout << "List size = " << paExtList -> Size() << endl << flush;
for (jj=1; jj<=paExtList->Size(); jj++)
{
CATBaseUnknown * pInt = (*paExtList)[jj] ;
if ( NULL != pInt )
{
rc = pInt -> QueryInterface(IID_CATIOsmExtension,
(void**) &piExtensionOnBase);
pInt -> Release();
pInt = NULL ;
...
piExtensionOnBase -> GetID(pExtId);
cout << "Extension ID = " << pExtId.ConvertToChar() << endl << flush;
piExtensionOnBase -> Release();
piExtensionOnBase = NULL;
}
}
delete paExtList;
paExtList = NULL;
...
|
Scanning the new list returned from QueryAllExtensions shows
that the only remaining extension on the base feature is:
List size = 1 Extension ID = CAAOsmChildrensNovel
[Top]
See the referenced article [6] for a detailed description of the steps to go through when saving the document.
Note that the opened catalog documents do not need to be removed from the session.
[Top]
This use case has demonstrated how to add, remove, retrieve extensions on a base feature. These operations are possible thanks the CATIOsmExtendable interface implemented.
AddExtension , is the method to add an extension to a base
feature. The CATRsc file associated with the feature extension type should
be in correspondance with your code otherwise, the method fails:ExtensionFeature.Extends key of the resource file
ExtensionFeature.Container key of the resource file.RemoveApplicativeExtensions,
is the method to remove an extension to a base feature. QueryExtension, QueryAllExtensions, are two
methods to retrieve a specific extension instance, or to retrieve all the
feature extensions of the base feature. [Top]
| Version: 1 [Feb 2001] | Document created |
| Version: 2 [Sep 2003] | Update to add a link to the "Creating Features in an App. Cont." article |
| Version: 3 [Feb 2005] | Document updated to integrate the new feature extension API |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2001, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.