|
This task shows you how to import to a CATPart or CATProduct
document
the data contained in a STEP AP203 / AP214 file.
It is also possible to insert a STEP file as an existing component in a
CATProduct. |
 |
Regarding AP214, both STEP AP 214 IS and STEP AP 214 DIS files are read.
|
|
The table entitled What about the
elements you import ?
provides information on the entities you can import.
You can find further information in the Advanced Tasks:
and in the Customizing
STEP Settings chapter.
Statistics about each import operation can be found in the
report file and the error file.
|

|
-
Depending on your configuration:
Click the Open icon
 or select the File > Open command.
or select the File > Open command.
The File Selection dialog box is displayed. |
| or |
|
Insert/Existing component command.
The File Selection dialog box is displayed. |
-
Set the .stp or .step extension in the Files of type
field.
| This displays all .stp or .step files contained in the selected
directory : |
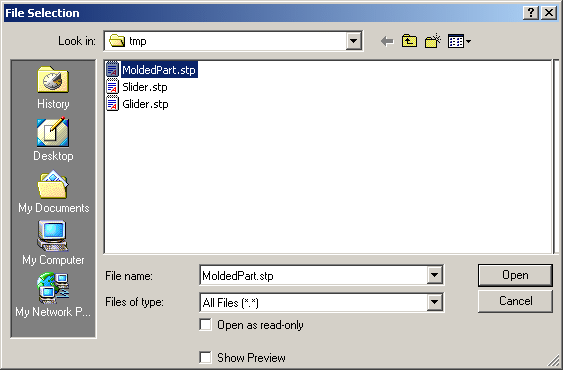 |
-
Select the .stp or .step file of your choice
(MoldedPart.stp, in our example) and click Open.
 |
| A progress bar is displayed. |
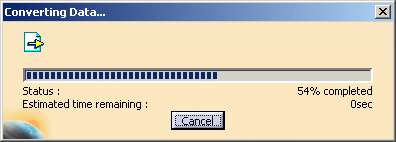 |
| You can use the Cancel button to interrupt the transfer at any
time. |
|
 |
What is then displayed depends on the contents of the STEP file.
- For the File/Open command:
- If the STEP file contains a normalized assembly structure,
a CATProduct document is created.
- If the STEP file does not contain any geometrical and
topological data,
the components will be visible only in the Specification Tree.
- If the STEP file contains also geometrical and topological data,
all the components will be present in the Geometry Space and in the
Specification Tree.
- If the STEP file contains only geometrical and topological data,
a CATPart document is created.
The geometrical elements of the faces, which could not be
transferred,
are created in the NO SHOW space. In the NO SHOW space, you can
visualize the Surface supports and the 3D Curves).
- For the Insert/Existing component command:
- if the STEP file contains no assembly information, it is
converted to a CATPart,
- if the STEP file contains assembly information, it is converted
to a CATProduct
referencing several CATPart documents.
The resulting document is inserted in the current CATProduct
document,
and the graphic window is updated (specification tree and geometry).
|
|
 |
- The reference to the STEP file is lost, so any update of the STEP file
will have no effect
in the CATProduct.
|
| |
- For both commands:
- The reference planes are hidden.
- A Geometrical Set is always created. It may be empty:
- it will contain the valid surfaces imported, if any.
- it is empty if there is no valid surfaces, e.g. when the element
imported is a solid,
or when all surfaces are invalid.
- invalid surfaces are sent to a specific Geometrical Set
(FaceKO#xxx)
|
|
Several STEP options can be customized:
|
|
 |
|
After the recovery of STEP files, the system generates:
-
a report file (name_of_step_file.rpt) where you
can find references about the quality of the transfer
-
and an error file (name_of_step_file.err) .
These files are created in a location referenced by the
CATReport variable. Its default value is
-
Profiles\user\Local
Settings\Application
Data\Dassault
Systemes\CATReport
on Windows (user being you logon id)
-
and $HOME/CATReport on UNIX.
|
 |
Always check the report and
error files after a conversion !
Some problems may have occurred without been visually highlighted. |
|
|
Example of a report file
Note that the conversion summary in the report file takes
assemblies into account.

Legend
- OK = Transferred
- KO = Not Transferred
- NS = Unsupported
- OUT = Out Of Size
"OUT" entities are OUT of model size. Most of the time, these
entities are curves
and they are out of the V5 model space. These entities are not
created. |
- DEG = Degenerated
- "DEG" entities are degenerated entities. They are solids
(MANIFOLD_SOLID_BREP) or
Shells (OPEN_SHELL), or Curves (LINE, CIRCLE,...).
Degenerated solids are incomplete solids (at least one Face misses)
|
- INV = Invalid
"INV" entities are Invalid entities, that is to say their
description within the STEP file
is invalid (STEP syntax rules are not respected,...). These entities
are not created. |
|
|
Example of error file:
E:\Report\pm6-hc-214.err
Input FileName : G:\Equipe_STEP\STEP\PDES-Prostep\Tr8\Prod\pm6-hc-214.stp
Output FileName :
============================================
*** = Processing new independent element
* = Intermediate processing
!! = Independent element K.O.
! = Intermediate error
--------------------------------------------
<I> = Information
<W> = Warning
<E> = Error
--------------------------------------------
[0000] = Message identifier : 0000
[T=xxx] = Entity Type Step : xxx
[#0000] = Entity identifier number : 0000
============================================
Actual display level : Customer
|
| |
Report messages
|
| |
Here are some of the messages that may appear:
- Too many cuts on face boundary.
Tip : Use topological reduction option (in IGES) or curve optimization (in
IGES or STEP) - see User's Guide
These options are accessible via Tools/Options/Compatibility/STEP
dialog boxes, in
the Continuity optimization of curves and surfaces section.
Select the Advanced optimization option and push the
Parameters... button.
For more information, click on the link on STEP above.
- <W> [0904] The face #xx was splitted into nn CATIA V5 faces
This message indicates that a STEP face has been split into several
V5 faces to comply with V5 data structure.
|
| |
When the Continuity optimization of curves and
surfaces/Advanced
optimization option in
Tools/Options/Compatibility/STEP is active, the following warning
messages may appear in the report file:
- The BSpine Surface is not C1: Approximation of the surface is
impossible!
This is just a warning, the surface is imported but is not approximated.
- The deformation found of the surface approximation (which is
calculated by isoparameters) is : xx millimeters.
This indicates that the real deformation found is higher than the
Deformation value
you have entered in the Parameters box and that the
approximation could not be performed.
When this occurs for several entities, you will find the following
information message at the end of the report file:
- For a better approximation of BSpline surfaces, you can use a "Curves
and surfaces approximation"
Deformation value of at least : xx millimeters
You can enter this value in the Parameters box of the
Continuity optimization of curves and surfaces/Advanced
optimization option in Tools/Options/Compatibility/STEP.
|
|
Shape Representation |
geometrically
bounded
wireframe |
geometrically
bounded
surface |
edge-based
wireframe |
shell-based
wireframe |
manifold
surface |
faceted
brep |
advanced
brep |
|
High Level Entities |
geometric_curve_set |
geometric_set |
edge_based_
wireframe_model |
shell_based_
wireframe_model |
shell_based_
surface_model |
faceted_brep
brep_with_voids |
manifold_solid_brep
brep_with_voids |
|
Entity |
 |
|
Point |
cartesian_point |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
NI |
I |
|
point_on_curve |
NI |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
|
point_on_surface |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
|
point_replica |
NI |
NI |
NI |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
|
degenerate_pcurve |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
| |
|
Curve |
line |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
circle |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
ellipse |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
hyperbola |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
parabola |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
polyline |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
b_spline_curve (+ rational)
b_spline_curve_with_knots |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
uniform_curve (+rational) |
NI |
NI |
NI |
NI |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
|
quasi_uniform_curve (+rational) |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
bezier_curve |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
trimmed_curve |
I |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
composite_curve |
I |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
composite_curve_on_surface |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
boundary_curve
outer_boundary_curve |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
pcurve |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
|
surface_curve |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
|
offset_curve_3D |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
NI |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
|
curve_replica |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
NI |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
| |
|
Surface |
plane |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
NI |
I |
|
cylindrical_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
conical_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
spherical_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
toroidal_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
degenerate_toroidal_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
surface_of_linear_extrusion |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
surface_of_revolution |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
b_spline_surface
b_spline_surface_with_knots |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
uniform_surface |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
|
quasi_uniform_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
bezier_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
rectangular_trimmed_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
curve_bounded_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
rectangular_composite_surface |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
offset_surface |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
|
surface_replica |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
Topology |
vertex_point |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
edge_curve |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
oriented_edge |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
vertex_loop |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
|
poly_loop |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
|
edge_loop |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
I |
N/A |
I |
|
face_bound
face_outer_bound |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
NI |
I |
|
face_surface |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
I |
N/A |
|
advanced_face |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
NI |
I |
|
oriented_face |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
|
vertex_shell |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
wire_shell |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
connected_edge_set |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
open_shell |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
N/A |
|
oriented_open_shell |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
closed_shell |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
NI |
I |
|
oriented_closed_shell |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
NI |
I |
|
manifold_solid_brep |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
|
brep_with_voids |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
|
faceted_brep |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
I |
N/A |
 or select the File > Open command.
or select the File > Open command.


![]()