The Chordal Fillet command is used
to control the width of the fillet (distance between the 2 rolling
edges) which is also called as chordal length.
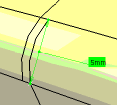
This command allows you to define two types of variation in the chordal fillet:
- Cubic
- Linear
This task shows you how to create chordal fillets.
Open the
Chordal_Fillet.CATPart
document.
To perform this task in
a different workbench like FMP,
create a cube.
-
Click Chordal Fillet
 in the Dress-Up Features toolbar (Fillets
sub-toolbar).
in the Dress-Up Features toolbar (Fillets
sub-toolbar).
The Chordal Fillet Definition dialog box is displayed. The default options let you define a cubic variation of the chordal fillet.
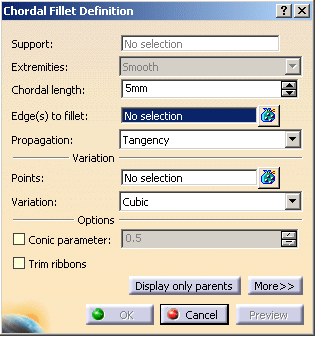
For Part Design workbench, click
Chordal Fillet
![]() .
.
For Generative Shape Design workbench,
click
Chordal Fillet
![]() .
.
The Support and Extremities fields are not seen in the Part Design workbench.
-
Select the edge to be filleted. You can define chordal fillets on closed edges.
The application detects both the vertices and displays two identical chordal lengths.
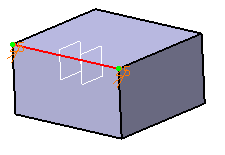
-
Double-click the chordal length to access the Parameter Definition dialog box. For example, enter 50mm.
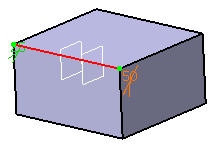
-
Click OK in the Parameter Definition dialog box.
-
Click the
 icon
of the
Points field in the Chordal Fillet Definition
dialog box. Select
Variable_Plane in the specification tree or geometry.
icon
of the
Points field in the Chordal Fillet Definition
dialog box. Select
Variable_Plane in the specification tree or geometry.
You can define a fillet with variable width by specifying the intermediate points.
-
Double-click Variable_Plane chordal length in geometry. For example, enter 20mm in the Parameter Definition dialog box.
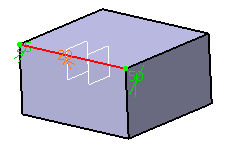
-
Click OK in Chordal Fillet Definition dialog box. The chordal fillet is created as seen:
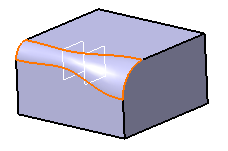
You can select the
Conic parameter check box. This option allows you to
vary the section of the fillet.
For a parameter between or equal to:
-
0.5, the resulting curve is a parabola.
-
0 < parameter < 0.5, the resulting curve is an arc of an ellipse.
-
0.5 < parameter < 1, the resulting curve is a hyperbola.
-
Conical fillets do not handle twist configurations. If a twist is detected, the fillet operation fails.
-
If the fillet surface curvature is lower than the support curvature, fillet surface relimitation may fail. In such cases, the conic parameter has to be decreased.
Limiting Elements
-
To edit this fillet, double-click EdgeFillet.1 in the specification tree or geometry. Click the More>> button to access the Limiting element(s) option.
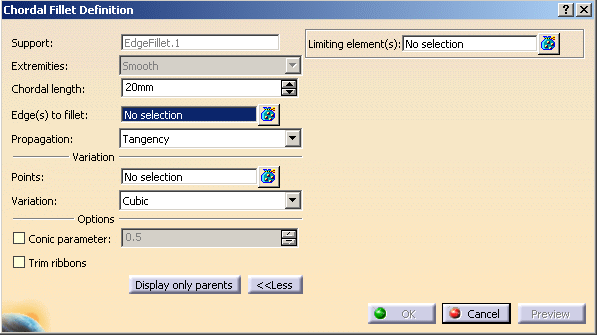
-
Click the
 icon of
Limiting element(s) field. Select Limit_Plane in the
specification tree or geometry.
icon of
Limiting element(s) field. Select Limit_Plane in the
specification tree or geometry.
-
Click OK. The variable radius fillet is trimmed to Limit_Plane. The final part looks like this:
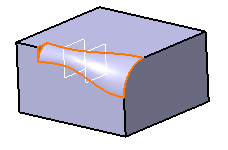
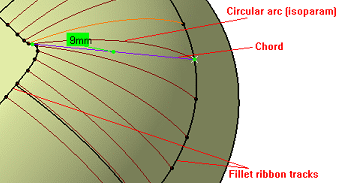
-
The chord length is measured using the isoparams (circular arcs).
-
The fillet surface respects the specified chord length. The chord length is measured using the circular arcs.
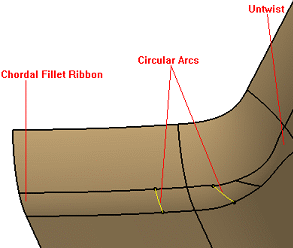
-
Some faces are created to correct the twists. In such a case, the corresponding warning message is displayed. Such untwisted surfaces in general do not satisfy the chord length constraint.
-
The constant chordal fillet should end in a tip, if the support surfaces are becoming tangent.
-
The constant chordal fillet cannot compute a fillet, if the support surfaces become tangent.
-
You should use variable chordal fillet with very small /zero radius at the location where the support surfaces become tangent. Constant chord fillet cannot handle such cases.
Chordal Fillet Dialog Box
Points
-
Contextual commands for creating the points you need are available from the Points field. Right-click in the Points field to see the contextual menu:

-
Create Point: For more information, see Creating Points.
-
Create Midpoint: Creates the midpoint of the line you select.
-
Create Endpoint: Creates the endpoint of the line you select.
-
Create Plane: For more information, see Creating Planes.
-
Create Intersection: For more information, see Creating Intersections.
-
Create Projection: For more information, see Creating Projections.
If you create any of these elements, the application displays the corresponding element detail in the Points field. Click the icon of the Points
field to edit the corresponding element.
icon of the Points
field to edit the corresponding element.
-
-
To add additional points on the edge to be filleted, you can also select planes. The application computes the intersections between these planes and the edge to determine the useful points.
-
Points can also be added by selecting the 3D points.
Limiting Elements
-
It is possible to use one or more limiting elements.
-
Contextual commands for creating the limiting elements you need are available in the Limiting element(s) field. Right-click in the Limiting element(s) field to see the contextual menu:
-
Create Point: For more information, see Creating Points.
-
Create Midpoint: Creates the midpoint of the line you select.
-
Create Endpoint: Creates the endpoint of the line you select.
-
Create Plane: For more information, see Creating Planes.
-
XY Plane: The XY plane of the current coordinate system origin (0,0,0) becomes the limiting element.
-
YZ Plane: The YZ plane of the current coordinate system origin (0,0,0) becomes the limiting element.
-
ZX Plane: The ZX plane of the current coordinate system origin (0,0,0) becomes the limiting element.
-
Create Intersection: For more information, see Creating Intersections.
-
Create Projection: For more information, see Creating Projections.
-
Create Join: Joins surfaces or curves. for more information, see Joining Surfaces or Curves.
-
Create Extrapol: Extrapolates surface boundaries or curves. For more information, see Extrapolating Surfaces and Extrapolating Curves.
If you create any of these elements, the application displays the corresponding element detail in the Limiting element(s) field. Click the
 icon of the Points
field to edit the corresponding element.
icon of the Points
field to edit the corresponding element. -
-
You can create limiting elements by clicking the edge to be filleted. The application displays this element as a blue disk.
-
You can select points as limiting elements. These points must be located on the edge to be filleted and they must have been created using the On curve option available in the Point Definition dialog box.