 .
.
3D PLM Enterprise Architecture |
Middleware Abstraction |
Parsing XML Documents with SAXUsing a SAX parser to read XML documents, with or without validation |
| Use Case | ||
AbstractThis article shows how to create a SAX parser. It explains how to create your own handlers to trap SAX events and how to register these handlers with the SAX parser. It shows you how to parse an XML document, with or without validation. |
This use case shows how to parse XML documents using the SAX API. You will learn to create two different kinds of event handlers for SAX: error handlers are invoked to process errors raised by the parser if the XML input is not well-formed or is invalid; document handlers are invoked when the parser encounters the most common XML constructs, such as elements, text or processing instructions. You will learn how to register your handlers with the parser. Finally, the use case will show you how to run the SAX parser configurated with your handlers to parse a file with or without validation.
[Top]
The CAAXMLSAXCount Use Case is a use case of the CAAXMLParser.edu framework that illustrates XMLParser framework capabilities.
[Top]
This use case parses an existing XML file and collects statistics about its contents: number of elements, number of attributes, number of characters, number of white space characters, number of processing instructions. Upon completion, it will print a report with these statistics in the console.
Element count = 4 Attribute count = 9 Character count = 41 Ignorable white space count = 0 Processing instruction count = 0 |
[Top]
To launch CAAXMLSAXCount, you will need to set up the build time environment, then compile CAAXMLSAXCount along with its prerequisites, set up the run time environment, and then execute the use case [1].
The use case should be launched as follows from the command line:
CAAXMLSAXCount [-v] <filepath>
where <filepath> is the path of the XML file, which
will be parsed.
A sample XML file is provided with the use case. To use it, launch the following command from the command line:
| Windows | CAAXMLSAXCount
InstallRoot\OS\resources\xml\CAAXMLSAXCount\CAAXMLSAXCount.xml |
| Unix | CAAXMLSAXCount
InstallRoot/OS/resources/xml/CAAXMLSAXCount/CAAXMLSAXCount.xml |
where:
InstallRoot is the directory in which you have
installed the run time part or the product lineOS is the directory containing the installed code
aix_a for 32-bit AIXhpux_b for HP-UXsolaris_a for Solarisintel_a for 32-bit Windowswin_b64 for 64-bit Windows[Top]
The CAAXMLSAXCount use case is made of several classes located in the CAAXMLSAXCount.m module of the CAAXMLParser.edu framework:
| Windows | InstallRootDirectory\CAAXMLParser.edu\CAAXMLSAXCount.m\ |
| Unix | InstallRootDirectory/CAAXMLParser.edu/CAAXMLSAXCount.m/ |
where InstallRootDirectory is the directory where the
CAA CD-ROM is installed.
[Top]
To create a SAX parser, implement and register event handlers with this parser, and parse a file, there are seven main steps:
| # |
Step |
|---|---|
| 1 | Implement a V5 Document Handler Component |
| 2 | Implement a V5 Error Handler Component |
| 3 | Create a V5 SAX Component |
| 4 | Create and Configure a V5 SAX Parser |
| 5 | Instantiate the Document Handler and Error Handler Components and Register Them With the Parser |
| 6 | Parse the XML File |
| 7 | Manage Errors |
[Top]
The SAX API uses an event-oriented API to process XML documents. The
XML SAX parser reads XML documents sequentially and invokes callback
functions to indicate the XML construct it comes across. Each invocation
is called a SAX event. The SAX API defines V5 interfaces, which specify
the signature of the SAX callback functions and group them per theme.
The CATISAXDocumentHandler interface defines functions, which
describe the most common XML constructs found in an XML document: start
of an document, end of an document, start of an element, end of an
element, characters, processing instruction, white space. Other SAX
interfaces (CATISAXDTDHandler, CATISAXErrorHandler, CATISAXEntityResolver)
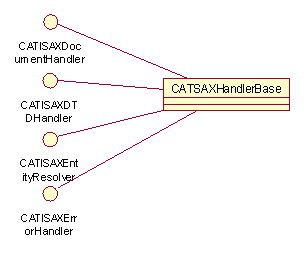
define additional events. To make the work easier for the developer, the
SAX API provides a CATSAXHandlerBase component, which already
provides an empty implementation of all the SAX interfaces.  .
.
Therefore, to write a SAX document handler, all you need to do is to create a new V5 component which inherits from CATISAXDocumentHandler and override the methods to answer to the events, which are relevant to your application. The following code declares and defines a CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler V5 component, which inherits from CATSAXHandlerBase and partially re-implements CATISAXDocumentHandler.
// CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler.h
#include "CATSAXHandlerBase.h"
class CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler : public CATSAXHandlerBase {
CATDeclareClass;
public:
...
// Override the default implementation of the
// CATISAXDocumentHandler methods we are interested in.
virtual HRESULT Characters(
const CATUnicodeString & iCharacters);
virtual HRESULT EndDocument();
...
};
|
// CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler.cpp #include "CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler.h" // Declare the class as a V5 component derived from CATSAXHandlerBase CATImplementClass( CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler, Implementation, CATSAXHandlerBase, CATnull ); // Implement the CATISAXDocumentHandler interface #include "TIE_CATISAXDocumentHandler.h" TIE_CATISAXDocumentHandler(CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler); |
The next step is to provide an implementation for each of the SAX
events you want to catch. The following code shows how the Characters
event callback function is implemented.
// CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler.cpp
HRESULT CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler::Characters(
const CATUnicodeString & iCharacters) {
// This event is sent by the CATISAXParser when a XML text is parsed
_characterCount += iCharacters.GetLengthInChar();
return S_OK;
}
|
This method counts the number of
characters in the text nodes of the XML document. The method receives
the text node in its iCharacters argument, of type CATUnicodeString.
The size of the CATUnicodeString is computed with GetLengthInChar
and added to the _characterCount instance variable.
[Top]
The CATISAXErrorHandler interface defines functions, which are called by the SAX parser when an error occurs. There are three error functions, corresponding to the severity of the error:
To write a SAX error handler, you need to create a new V5 component, which inherits from CATISAXErrorHandler and override the methods to answer to the events, which are relevant to your application. The use case declares a CAAXMLSAXCountErrHandler V5 component, which inherits from CATSAXHandlerBase and re-implements CATISAXErrorHandler. For concision, the code to do that not reproduced here as it is nearly identical to the CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler code from the previous section.
The next step is to provide an implementation for each of the SAX
events you want to catch. To ask the parser to ignore a recoverable
error and proceed, the implementation must return S_OK. To ask
the parser to abort, the parser must return E_FAIL.
// CAAXMLSAXCountErrHandler.cpp
HRESULT CAAXMLSAXCountErrHandler::Error (
CATSAXParseException* iException) {
...
// Let the parser continue the parsing (if we returned E_FAIL, parsing would stop)
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT CAAXMLSAXCountErrHandler::FatalError (
CATSAXParseException* iException) {
...
// Stop the parsing. The CATISAXParser will stop anyway since this is a FatalError.
return E_FAIL;
}
|
[Top]
... // CAAXMLSAXCountMain.cpp CATIXMLSAXFactory_var factory; HRESULT hr = ::CreateCATIXMLSAXFactory(factory); ... |
To work with SAX, you need to instantiate the V5 SAX component. The
V5 SAX component can be created by calling the CreateCATIXMLSAXFactory
global function. This function returns a V5 handler on the CATIXMLSAXFactory
interface, which is the main interface for the V5 SAX component. Using
this interface you will be able to create SAX1 and SAX2 parsers and to
create input source to feed XML to the parser. Note that the code above
does not specify the CLSID of the component to use, so the default SAX
component (XML4C3) will be used. See [3] and [4] if you want to use another V5 SAX component.
[Top]
...
CATListOfCATUnicodeString options;
CATListOfCATUnicodeString optionValues;
options.Append("CATDoValidation");
if (isValidating) {
optionValues.Append("true");
} else {
optionValues.Append("false");
}
CATISAXParser_var parser;
hr = factory->CreateParser(parser, options, optionValues);
... |
To create a SAX1 parser, one simply invokes the CreateParser
on the CATIXMLSAXFactory object. There are two kinds of SAX1
parsers: non-validating SAX1 parsers and validating SAX1 parsers. You
need to decide at creation time what kind of parser you want to create
using the "CATDoValidation" option. Options are passed to the
parser using two CATListOfCATUnicodeStrings. The first one
contains the option names, the second one contains the option values.
See [3] and [4] for information
about validating versus non-validating parser.
[Top]
The SAX1 parser created in the previous section is not yet usable as
it does not yet know any other objects to which it can send the events
it generates. The SAX1 parser can accept up to four event handlers (one
for each event interface), as shown in the diagram below. 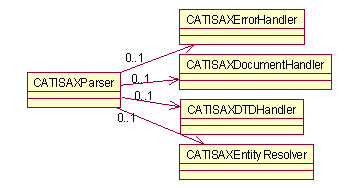
... CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler *docHandlerImpl = new CAAXMLSAXCountDocHandler(); CATISAXDocumentHandler_var docHandler = docHandlerImpl; docHandlerImpl->Release(); docHandlerImpl = NULL; CAAXMLSAXCountErrHandler *errHandlerImpl = new CAAXMLSAXCountErrHandler(); CATISAXErrorHandler_var errHandler = errHandlerImpl; errHandlerImpl->Release(); errHandlerImpl = NULL; ... |
To instantiate the document handler and the error handler you have
defined in the previous section, simply
do a new of the main implementation class, then get an interface
handle of the right type on the component.
... hr = parser->SetDocumentHandler(docHandler); ... hr = parser->SetErrorHandler(errHandler); ... |
To register your document handler, call the SetDocumentHandler
method of the CATISAXParser interface. To register your error
handler, call the SetErrorHandler method of the CATISAXParser
interface. Passing NULL_var to these methods unregisters the
previously registered handlers.
[Top]
hr = parser->Parse(filePath); ... |
To parse the XML file, call the Parse method of the CATISAXParser
interface. Pass the path of the file to read as a parameter. The method
will read the file from top to bottom and generate the corresponding
events, calling your event handlers for all the events you want to
manage.
[Top]
The XMLParser framework uses the HRESULT / CATError mechanism to
manage errors. Make sure to use the CATError::CATGetLastError
to obtain all the available error diagnostics when using XMLParser. More
information about V5 error management is available here [2]
and [4].
[Top]
This use case shows you how to parse XML documents using the SAX API.
[Top]
| [1] | Building and Launching a CAA V5 Use Case |
| [2] | Managing Errors Using HRESULT |
| [3] | Using XML in V5 |
| [4] | XML Tips and Tricks |
| [Top] | |
| Version: 1 [May 2005] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2005, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.