3D PLM Enterprise Architecture
|
3D Visualization
|
Making a Component Displayable With CATI3DGeoVisu
Implementing CATI3DGeoVisu and CATIModelEvents to enable a geometric
component to be displayed in a viewer |
| Use Case |
Abstract
This article discusses the CAAVisGeoModel use case. This use case
explains how geometric components can provide a representation to be
displayed in a viewer.
|
What You Will Learn With This Use Case
This use case is intended to show how to implement the CATI3DGeoVisu
interface to make a geometric component displayable in a 3D viewer, and how to
implement the CATIModelEvents interface to refresh the representation
according to model updates.
[Top]
The CAAVisGeoModel Use Case
CAAVisGeoModel is a set of use cases of the CAAVisualization.edu framework
that illustrates Vizualization framework capabilities.
[Top]
What Does CAAVisGeoModel Do
CAAVisGeoModel contains a series of C++ classes, each of them being an
extension of a component representing a geometric component, such as a
point, a line, a circle, or an ellipse. Each extension implements the CATI3DGeoVisu
interface to make the corresponding component displayable in a 3D viewer. This
article focuses on the way the circle component implements CATI3DGeoVisu.
In addition, a single extension class implements the CATIModelEvents
interface for all the geometric components. It is also described.
[Top]
How to Launch the CAAVisGeoModel
See the section entitled "How to Launch the CAAGeometry Use Case"
in the "The
CAAGeometry Sample" use case for a detailed description of how this use
case should be launched. For the specific scenario :
Launch CATIA. When the application is ready, follow scenarios described
below:
- In the Start menu choose Infrastructure and click CAA V5:
Geometrical Creation
- In the Insert menu choose Point
- Create three points
- In the Insert menu choose Plane
- Select the three points
- In the Insert menu choose Circle
- Select the plane first and then click right on the screen
[Top]
Where to Find the CAAVisGeoModel Code
CAAVisGeoModel code is located in the CAAVisGeoModel.m use case module of the
CAAVisualization.edu framework:
| Windows |
InstallRootDirectory\CAAVisualization.edu\CAAVisGeoModel.m |
| Unix |
InstallRootDirectory/CAAVisualization.edu/CAAVisGeoModel.m |
where InstallRootDirectory is the root directory of your CAA V5
installation.
CAAVisGeoModel includes the following files for the circle component:
| LocalInterfaces directory |
| CAAEVisVisuCircle.h |
Header file for the circle component extension class that implements CATI3DGeoVisu |
| CAAEVisModelEvents.h |
Header file for the common component extension class that implements CATIModelEvents |
| src directory |
| CAAEVisVisuCircle.cpp |
Source file for the circle component extension class that implements CATI3DGeoVisu |
| CAAEVisModelEvents.cpp |
Source file for the common component extension class that implements CATIModelEvents |
[Top]
Step-by-Step
To implement CATI3DGeoVisu and CATIModelEvents, there are four
main steps:
- Creating the Header File of CAAEVisVisuCircle
- Creating the Source File of CAAEVisVisuCircle
- Implementing the BuildRep Method of CATI3DGeoVisu
- Implementing the CATIModelEvents Interface
[Top]
Creating the Header File of CAAEVisVisuCircle
The CAAEVisVisuCircle header file is as follows.
#include "CATExtIVisu.h"
class CAAEVisVisuCircle : public CATExtIVisu
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAAEVisVisuCircle();
virtual ~CAAEVisVisuCircle();
virtual CATRep * BuildRep();
private :
CAAEVisVisuCircle(const CAAEVisVisuCircle &iObjectToCopy);
};
|
CAAEVisVisuCircle derives from the CATExtIVisu adapter that provides
code for the CATI3DGeoVisu interface methods. As any class that makes up
a component, its header file includes the CATDeclareClass macro.
The BuildRep method is the only one to redefine. Note that the copy
constructor is declared as private, and is not implemented. This prevents the
compiler from creating a public one without you know. This is to prevent clients
from creating instances from an existing one, that they normally should not
handle, except using interface pointers.
[Top]
Creating the Source File of CAAEVisVisuCircle
The CAAEVisVisuCircle source file is as follows.
#include "CAAEVisVisuCircle.h"
#include "CAAISysCircle.h"
#include "CAT3DCustomRep.h"
#include "CAT3DArcCircleGP.h"
#include "TIE_CATI3DGeoVisu.h"
TIE_CATI3DGeoVisu(CAAEVisVisuCircle);
CATImplementClass(CAAEVisVisuCircle, DataExtension, CATBaseUnknown, CAASysCircle);
CAAEVisVisuCircle::CAAEVisVisuCircle() {}
CAAEVisVisuCircle::~CAAEVisVisuCircle() {}
CATRep * CAAEVisVisuCircle::BuildRep()
{
...
}
|
The main points of this source file are:
- CAAEVisVisuCircle implements the CATI3DGeoVisu interface:
this is expressed thanks to the
TIE_CATI3DGeoVisu macro
- CAAEVisVisuCircle implements the CATI3DGeoVisu interface for
the CAASysCircle component as a data extension. This is expressed
using the
CATImplementClass macro
- The BuildRep method is the only redefined method of CATI3DGeoVisu.
It should return a pointer to the circle representation, that is, a pointer
to a CAT3DRep
[Top]
Implementing the BuildRep Method of CATI3DGeoVisu
There are two possibilities for creating the representation of a circle, that
is, using the CAT3DArcCircleRep class, or using a custom representation.
This latter is detailed here.
- Declaring the representation to return
CATRep * CAAEVisVisuCircle::BuildRep()
{
CAT3DCustomRep *pCircleRep = NULL;
...
|
The CAT3DCustomRep class can accommodate any kind of
representation(s).
- Retrieving the circle parameters
...
CAAISysCircle * piSysCircle = NULL;
HRESULT rc = QueryInterface(IID_CAAISysCircle, (void**)&piSysCircle);
if (SUCCEEDED(rc))
{
CATMathPoint center;
float radius;
CATMathVector normal, axis;
piSysCircle->GetCenter(center);
piSysCircle->GetRadius(radius);
piSysCircle->GetPlane(normal, axis);
piSysCircle->Release();
...
|
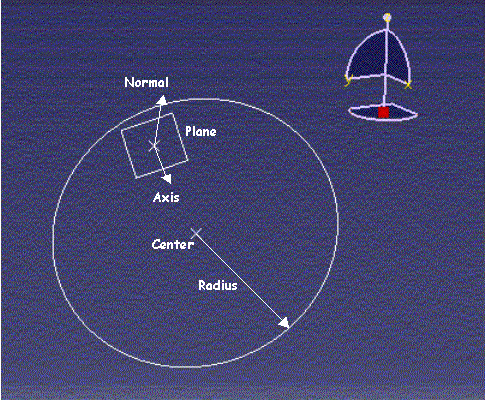 |
The circle component implements the CAAISysCircle interface [1].
This is a type interface that enables to set and retrieve the
parameters that make this component a circle: its center and radius,
and the normal and axis vectors of the plane in which it lies. Once
the pointer to CAAISysCircle is not any longer needed, it is
released. |
- Creating the graphic primitive for the circle
...
CAT3DArcCircleGP * pCircleGp = new CAT3DArcCircleGP(center, normal, radius, axis);
...
|
The circle graphic primitive is an instance of CAT3DArcCircleGP.
Its constructor needs the four parameters retrieved from the circle
component.
- Creating and filling in the representation
...
pCircleRep = new CAT3DCustomRep();
CATGraphicAttributeSet circleGa;
pCircleRep->AddGP(pCircleGp,circleGa);
...
|
The circle representation is created as a CAT3DCustomRep instance.
Is is filled in thanks to the AddRep method with the graphical
primitive and a set of graphic attributes featuring their default values.
- Creating the circle bounding element and assigning it to the
representation
...
CAT3DBoundingSphere circleBe(center,radius);
pCircleRep->SetBoundingElement(circleBe);
...
|
In order to increase display performance, any representation should have
a bounding element that is first asked to determine whether the associated
representation should be displayed in the current view port. This bounding
element is chosen as a CAT3DBoundingSphere instance defined using the
circle center and radius. The SetBoundingElement method assigns
it to the circle representation.
- Returning the created representation
...
}
return pCircleRep;
}
|
The circle is now ready for display.
[Top]
Implementing the CATIModelEvents Interface
CAAVisModelEvents implements the CATIModelEvents interface by
deriving from the CATExtIModelEvents adapter.
- Creating the header file.
#include "CATExtIModelEvents.h"
class CAAEVisModelEvents : public CATExtIModelEvents
{
CATDeclareClass;
public :
CAAEVisModelEvents();
virtual ~CAAEVisModelEvents();
private :
CAAEVisModelEvents(const CAAEVisModelEvents &iObjectToCopy);
};
|
As any class that makes up a component [2], its
header file includes the CATDeclareClass macro. None of the CATIModelEvents
methods needs to be redefined. Note that the copy constructor is declared as
private, and is not implemented. This prevents the compiler from creating a
public one without you know. This is to prevent clients from creating
instances from an existing one, that they normally should not handle, except
using interface pointers.
- Creating the source file.
#include "CAAEVisModelEvents.h"
#include "TIE_CATIModelEvents.h"
TIE_CATIModelEvents(CAAEVisModelEvents);
CATBeginImplementClass(CAAEVisModelEvents, DataExtension, CATBaseUnknown, CAASysPoint);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysSampRootObj);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysGeomRootObj);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysLine);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysEllipse);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysPlane);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysCircle);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysPolyline);
CATEndImplementClass(CAAEVisModelEvents);
CAAEVisModelEvents::CAAEVisModelEvents() {}
CAAEVisModelEvents::~CAAEVisModelEvents() {}
|
The main points of this source file are:
- CAAEVisModelEvents implements the CATIModelEvents
interface: this is expressed thanks to the
TIE_CATIModelEvents
macro
- CAAEVisModelEvents implements the CATIModelEvents
interface for several components, among which the CAASysCircle
component, as a data extension. Compared to the declaration of a single
component extension using
CATImplementClass, this is
expressed using three macros:
CATBeginImplementClass, that has the same signature
than CATImplementClass, and that namely declares that CAAEVisModelEvents
is a data extension of the CAASysPoint component, and that
OM-derives from CATBaseUnknownCATAddClassExtension to declare each additional
extended component, such as CAASysCircleCATEndImplementClass to close the extended component
declaration
- Since none of the CAAIModelEvents methods needs to be
redefined, the default constructor and the destructor are enough.
[Top]
In Short
This use case shows how to implement the CATI3DGeoVisu interface to
display a geometric component in a 3D viewer. CATI3DGeoVisu is
implemented in an extension class of the geometric component by deriving the
extension from the CATExtI3DVisu adapter, and redefining the BuildRep
method. BuildRep creates and returns the 3D representation that
stands for the geometric component in the visualization world using the
component geometric parameters.
To enable the representation of the geometric component to be refreshed when
the component is modified, the component should implement the CATIModelEvents
interface. This is done also using an extension, but can be done for a component
family in a single extension for the whole family. Usually, deriving from the CATExtIModelEvents
adapter is enough, and no method needs to be redefined.
[Top]
References
History
| Version: 1 [Feb 2000] |
Document created |
| [Top] |
Copyright © 2000, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.
