3D PLM Enterprise Architecture |
Middleware Abstraction - Object Modeler |
Creating ComponentsMaking objects that implement interfaces |
| Use Case | ||
AbstractThis article shows how to create CAA V5 components. |
This use case is intended to show you how to create CAA V5 components [1], that is, how to bundle several C++ classes that each implements one or several interfaces [2] and make that this set of classes acts and behaves as a single application object.
[Top]
CAASysGeoModelImpl is a use case of the CAASystem.edu framework that illustrates the System framework capabilities.
[Top]
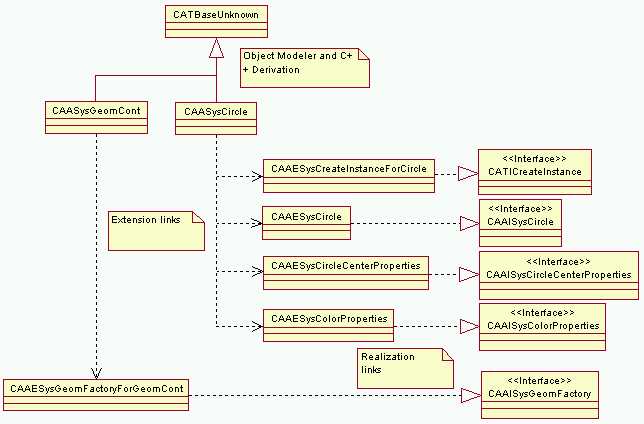
This use case includes the code for a set of components that stand for geometric objects. The circle is taken as example.

The circle component is made of the CAASysCircle main class, and of the CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle, CAAESysCircle, CAAESysCircleCenterProperties, and CAAESysColorProperties extension classes. CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle implements the CATICreateInstance interface to enable the component creation. CAAESysCircle implements the CAAISysCircle interface that is the circle type interface. CAAESysCircleCenterProperties implements the CAAISysCircleCenterProperties interface to manage the marker used to represent the circle center. CAAESysColorProperties implements the CAAISysColorProperties interface to manage the circle color. CAAESysCircle and CAAISysCircleCenterProperties are extension classes of the CAASysCircle class only, while CAAESysColorProperties is shared with other geometric components, such as the line, the polyline, and the ellipse. Refer to sharing extensions in [1].
In addition, the factory for the circle component is also described. The CAASysGeomCont main class that represents a container for geometric objects implements the CAAISysGeomFactory interface through a code extension class named CAAESysGeomFactoryForGeomCont [3].
Note: Extension links are shown as dashed arrows, and implementation to interface links are shown using the realization link symbol, made of a dash line ended using a triangle on the interface side.
[Top]
You first need to build CAASysGeoModelImpl. To do this, you will need to set up the build time environment, then compile CAASysGeoModelImpl along with its prerequisites as described in [5]. You cannot launch CAASysGeoModelImpl itself. CAASysGeoModelImpl is simply used by the CAASysUsingComp [4] use case.
[Top]
The CAASysGeoModelImpl use case is made of several classes located in the CAASysGeoModelComp.m for the component main classes and extension classes that implement CATICreateInstance, and CAASysGeoModelImpl.m module for the other extension classes. These modules belong to the CAASystem.edu framework:
| Windows | InstallRootDirectory\CAASystem.edu\ |
| Unix | InstallRootDirectory/CAASystem.edu/ |
where InstallRootDirectory is the directory where the CAA CD-ROM
is installed. The header files of shared classes are located in the
PrivateInterfaces directory of CAASystem.edu.
[Top]
To create a component such as CAASysCircle, there are nine main steps:
| # | Step | Where |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create the CAASysCircle component main class header file | ProtectedInterfaces\CAASysCircle.h |
| 2 | Create the CAASysCircle component main class source file | CAASysGeoModelComp.m\src\CAASysCircle.cpp |
| 3 | Create the CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle extension class header file | CAASysGeoModelComp.m\LocaInterfaces\CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle.h |
| 4 | Create the CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle extension class source file | CAASysGeoModelComp.m\src\CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle.cpp |
| 5 | Create the CAAESysCircle extension class header file | CAAESysCircle.h file |
| 6 | Create the CAAESysCircle extension class source file | CAAESysCircle.cpp file |
| 7 | Create the CAAESysCenterProperties extension class header file | CAAESysCircleCenterProperties.h file |
| 8 | Create the CAAESysCenterProperties extension class source file | CAAESysCircleCenterProperties.cpp file |
| 9 | Create the CAAESysColorProperties shared extension class header file | CAAESysColorProperties.h file |
| 10 | Create the CAAESysColorProperties shared extension class source file | CAAESysColorProperties.cpp file |
| 11 | Update the interface dictionary | CAASystem.edu.dico file |
[Top]
#include "CATBaseUnknown.h" //Needed to derive from CATBaseUnknown
#include "CAASysGeoModelComp.h" //To export the class
class ExportedByCAASysGeoModelComp CAASysCircle : public CATBaseUnknown
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAASysCircle();
virtual ~CAASysCircle();
private:
CAASysCircle(const CAASysCircle &iObjectToCopy);
|
The CAASysCircle class C++-derives from CATBaseUnknown. The CATDeclareClass
macro declares that the class CAASysCircle belongs to a component. Note
that the copy constructor is set as private. The class has a constructor and a
destructor only.
[Top]
#include "CAASysCircle.h"
CATImplementClass(CAASysCircle, Implementation, CATBaseUnknown, CATNull);
CAASysCircle::CAASysCircle() {}
CAASysCircle::~CAASysCircle() {}
|
The CATImplementClass macro declares that the CAASysCircle
class is a component main class thanks the Implementation keyword,
and OM-derives [6] from CATBaseUnknown. Any
component main class declared as an Implementation must C++-derive
and OM-derive from the same class, that must either be CATBaseUnknown or
another component main class. The component main class doesn't implement any
interface, but it could.
[Top]
#include "CATBaseUnknown.h" //Needed to derive from CATBaseUnknown
class CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle : public CATBaseUnknown
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle();
virtual ~CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle();
virtual HRESULT __stdcall CreateInstance(void **oppv);
private:
CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle(const CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle &iObjectToCopy);
};
|
The CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle extension class derives from CATBaseUnknown.
The CATDeclareClass macro declares that the class CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle
belongs to a component. The class has a constructor and a destructor, and
declares the CreateInstance method which is the only method of the CATICreateInstance
interface. Note that the copy constructor is set as private. This is very
important for extensions. Since extensions must never be directly instantiated
by client applications, this prevents the compiler from creating the copy
constructor as public without you know. This copy constructor is not implemented
in the source file.
[Top]
#include "CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle.h"
#include "CAASysCircle.h"
#include <CATErrorDef.h>
#include "TIE_CATICreateInstance.h"
TIE_CATICreateInstance(CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle);
CATImplementClass(CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle, CodeExtension, CATBaseUnknown, CAASysCircle);
CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle::CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle() {}
CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle::~CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle() {}
HRESULT __stdcall CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle::CreateInstance(void ** oppv)
{
CAASysCircle * pt = new CAASysCircle();
if (NULL == pt) return(E_OUTOFMEMORY);
*oppv = (void *)pt;
return(S_OK);
}
|
The CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle class states that it implements the
CATICreatInstance interface thanks to the TIE_CATICreateInsatnce
macro. This extension class is dedicated to the circle component, and the CATImplementClass
macro declares that the CAAESysCreateInstanceForCircle class is code
extension class, thanks to the CodeExtension keyword, and that it
extends the component whose main class is CAASysCircle. The third
parameter must always be set to CATBaseUnknown, makes no sense, and is
unused for extensions. The CreateInstance method instantiates the CAASysCircle
component main class. This method is called by the CATInstantiateComponent
global function that is used by client applications to instantiate the component
[4].
[Top]
#include "CATBaseUnknown.h" //Needed to derive from CATBaseUnknown
// Mathematics Framework
#include "CATMathPoint.h" //Needed by SetCenter & GetCenter
#include "CATMathVector.h" //Needed by SetPlanar & GetPlanar
class CAAESysCircle : public CATBaseUnknown
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAAESysCircle();
virtual ~CAAESysCircle();
// CAAISysCircle interface methods
virtual HRESULT SetCenter(const CATMathPoint & iCenter) ;
virtual HRESULT GetCenter(CATMathPoint & oCenter) const ;
virtual HRESULT SetRadius(const float iRadius) ;
virtual HRESULT GetRadius(float & oRadius) const ;
virtual HRESULT SetPlane (const CATMathVector & iNormal ,
const CATMathVector & iAxis );
virtual HRESULT GetPlane (CATMathVector & oNormal ,
CATMathVector & oAxis ) const;
private:
CAAESysCircle(const CAAESysCircle &iObjectToCopy);
private:
float _Radius ;
CATMathPoint _Center ;
CATMathVector _Normal ;
CATMathVector _Axis ;
};
|
The CAAESysCircle extension class derives from CATBaseUnknown.
The CATDeclareClass macro declares that the class CAAESysCircle
belongs to a component. The class has a constructor and a destructor, and
declares the methods of the CAAISysCircle interface, that set and get the
circle center, radius, and plane. Note that the copy constructor is set as
private. This is very important for extensions. Since extensions must never be
directly instantiated by client applications, this prevents the compiler from
creating the copy constructor as public without you know. This copy constructor
is not implemented in the source file. The circle data are its center, its
radius, the normal to its plane, and an axis of this plane.
[Top]
#include "CAAESysCircle.h"
#include "TIE_CAAISysCircle.h"
TIE_CAAISysCircle(CAAESysCircle);
CATImplementClass(CAAESysCircle, DataExtension, CATBaseUnknown, CAASysCircle);
CAAESysCircle::CAAESysCircle() : _Radius(0) {}
CAAESysCircle::~CAAESysCircle() {}
HRESULT CAAESysCircle::SetCenter(const CATMathPoint & iCenter)
{
_Center = iCenter ;
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT CAAESysCircle::SetRadius(const float iRadius)
{
_Radius = iRadius ;
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT CAAESysCircle::SetPlanar(const CATMathVector & iNormal,
const CATMathVector & iAxis)
{
_Normal= iNormal ;
_Axis = iAxis ;
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT CAAESysCircle::GetCenter(CATMathPoint & oCenter) const
{
oCenter = _Center ;
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT CAAESysCircle::GetRadius(float & oRadius) const
{
oRadius = _Radius ;
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT CAAESysCircle::GetPlanar(CATMathVector & oNormal ,
CATMathVector & oAxis) const
{
oNormal = _Normal ;
oAxis = _Axis ;
return S_OK;
}
|
The CAAESysCircle class states that it implements the CAAISysCircle
interface thanks to the TIE_CAAISysCircle macro. This extension
class is dedicated to the circle component, and the CATImplementClass
macro declares that the CAAESysCircle class is data extension class,
thanks to the DataExtension keyword, and that it extends the
component whose main class is CAASysCircle. The third parameter must
always be set to CATBaseUnknown, makes no sense, and is unused for
extensions. The CAAISysCircle interface methods are implemented as usual.
[Top]
#include "CATBaseUnknown.h" // Needed to derive from CATBaseUnknown
#include "CAAISysCircleCenterProperties.h" // Needed to have the marker type
class CAAESysCircleCenterProperties: public CATBaseUnknown
{
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAAESysCircleCenterProperties();
virtual ~CAAESysCircleCenterProperties();
virtual HRESULT GetMarkerType(CAAISysCircleCenterProperties::MarkerType & oMarkerType);
virtual HRESULT SetMarkerType(const CAAISysCircleCenterProperties::MarkerType iMarkerType);
private:
CAAESysCircleCenterProperties(const CAAESysCircleCenterProperties &iObjectToCopy);
private:
CAAISysCircleCenterProperties::MarkerType _MarkerType ;
};
|
The CAAESysCircleCenterProperties extension class derives from CATBaseUnknown.
The CATDeclareClass macro declares that the class CAACAAESysCircleCenterProperties
belongs to a component. The class has a constructor and a destructor, and
declares the GetMarkerType and SetMarkerType methods
of the CAAISysCircleCenterProperties interface. The marker type is set as
a private data member. Note that the copy constructor is set as private. This is
very important for extensions. Since extensions must never be directly
instantiated by client applications, this prevents the compiler from creating
the copy constructor as public without you know. This copy constructor is not
implemented in the source file.
[Top]
#include "CAAESysCircleCenterProperties.h"
#include "TIE_CAAISysCircleCenterProperties.h"
TIE_CAAISysCircleCenterProperties(CAAESysCircleCenterProperties);
CATImplementClass(CAAESysCircleCenterProperties, DataExtension, CATBaseUnknown, CAASysCircle);
CAAESysCircleCenterProperties::CAAESysCircleCenterProperties():
_MarkerType(CAAISysCircleCenterProperties::Dot)
{}
CAAESysCircleCenterProperties::~CAAESysCircleCenterProperties()
{}
HRESULT CAAESysCircleCenterProperties::GetMarkerType(CAAISysCircleCenterProperties::MarkerType & oMarkerType )
{
oMarkerType = _MarkerType ;
return (S_OK);
}
HRESULT CAAESysCircleCenterProperties::SetMarkerType(const CAAISysCircleCenterProperties::MarkerType iMarkerType)
{
_MarkerType = iMarkerType ;
return (S_OK);
}
|
The CAAESysColorProperties class states that it implements the CAAISysPointProperties
interface thanks to the TIE_CAAISysPointProperties macro. This
extension class is dedicated to the circle components, and the CATImplementClass
macro declares that the CAAESysPointProperties class is data extension
class, thanks to the DataExtension keyword, and that it extends the
component whose main class is CAASysCircle. The third parameter must
always be set to CATBaseUnknown, makes no sense, and is unused for
extensions. The CAAISysPointProperties interface methods are implemented
as usual.
[Top]
#include "CATBaseUnknown.h" // to derive from CATBaseUnknown
class CAAESysColorProperties: public CATBaseUnknown
{
// Used in conjunction with CATImplementClass in the .cpp file
CATDeclareClass;
public:
CAAESysColorProperties();
virtual ~CAAESysColorProperties();
virtual HRESULT GetColor( int &oRed, int &oGreen, int &oBlue) const;
virtual HRESULT SetColor(const int iRed, const int iGreen, const int iBlue);
private:
CAAESysColorProperties(const CAAESysColorProperties &iObjectToCopy);
private:
int _Red, _Green, _Blue,;
};
|
The CAAESysColorProperties extension class derives from CATBaseUnknown.
The CATDeclareClass macro declares that the class CAAESysColorProperties
belongs to a component. The class has a constructor and a destructor, and
declares the GetColor and SetColor methods of the CAAISysColorProperties
interface. The RGB color components are set as private data members. Note that
the copy constructor is set as private. This is very important for extensions.
Since extensions must never be directly instantiated by client applications,
this prevents the compiler from creating the copy constructor as public. This
copy constructor is not implemented in the source file.
[Top]
#include "CAAESysColorProperties.h"
#include "TIE_CAAISysColorProperties.h"
TIE_CAAISysColorProperties(CAAESysColorProperties);
CATBeginImplementClass(CAAESysColorProperties, DataExtension, CATBaseUnknown, CAASysCircle);
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysEllipse) ;
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysLine) ;
CATAddClassExtension(CAASysPolyline) ;
CATEndImplementClass(CAAESysColorProperties);
CAAESysColorProperties::CAAESysColorProperties()
: _Red(255),_Blue(255),_Green(255)
{}
CAAESysColorProperties::~CAAESysColorProperties() {}
HRESULT CAAESysColorProperties::SetColor(const int iRed, const int iGreen, const int iBlue)
{
if ( (iRed < 0) || (iRed > 255) ) return E_FAIL;
if ( (iGreen < 0) || (iGreen > 255) ) return E_FAIL;
if ( (iBlue < 0) || (iBlue > 255) ) return E_FAIL;
_Red = iRed ;
_Green = iGreen ;
_Blue = iBlue ;
return (S_OK);
}
HRESULT CAAESysColorProperties::GetColor(int & oRed, int & oGreen, int & oBlue) const
{
oRed = _Red;
oGreen = _Green;
oBlue = _Blue;
return (S_OK);
}
|
The CAAESysColorProperties class states that it implements the CAAISysColorProperties
interface thanks to the TIE_CAAISysColorProperties macro. This
extension class is shared by several components, and declares these components
thanks to the CATBeginImplementClass, CATAddClassExtension,
and CATEndImplementClass macros:
CATBeginImplementClass declares that the CAAESysColorProperties
class is a component extension class thanks the DataExtension
keyword, and that it extends the component whose main class is CAASysCircle.
The third parameter must always be set to CATBaseUnknown, makes no
sense, and is unused for extensions.CATAddClassExtension goes on declaring that CAAESysColorProperties
extends as a data extension the components whose main classes are CAASysEllipse,
CAASysEllispe, and CAASysPolyline.CATEndImplementClass ends the extended component list.The CAAISysColorProperties interface methods are implemented as usual.
[Top]
... CAASysCircle CATICreateInstance libCAASysGeoModelComp CAASysCircle CAAISysCircle libCAASysGeoModelImpl CAASysCircle CAAISysColorProperties libCAASysGeoModelImpl CAASysCircle CAAISysCircleCenterProperties libCAASysGeoModelImpl ... |
The interface dictionary declares that the CAASysCircle component implements the CAAISysCircle, CAAISysColorProperties, and CAAISysCircleCenterProperties, and that the code to load into memory to use these interfaces is located in the libCAASysGeoModelImpl shared library or DLL. Note that the component main class name is used to refer to the component in the interface dictionary, and never the extension class names. Note also that the shared library or DLL to associate with the component/interface pair is the one that contains the code created by the call to the TIE macro (This is generally the same library than the one that contains the interface implementation code, since the TIE macro is usually included in the extension class source file.) This is because when a client asks a component for an interface pointer, the TIE class is instantiated first, and it either retrieves the existing instance of the appropriate extension class, or otherwise instantiates it.
Top]
This use case shows how to create a component using a main class and extension classes. The main class declares the component inheritance and must C++-derive and OM-derive from CATBaseUnknown or from another component main class. Extension classes must directly or indirectly C++-derive from CATBaseUnknown, while OM-inheritance makes no sense for them. An extension class can be dedicated to a component or shared by several components. The interface dictionary declares the correspondence between the component, the interfaces it implements, and the shared library or DLL to load for each interface.
[Top]
| Version: 1 [Mar 2000] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2000, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.