
3D PLM PPR Hub Open Gateway |
CATIA - ENOVIA VPM V4 Interoperability |
File Based ImportImporting an assembly in Structure Exploded mode |
| Use Case | ||
AbstractThis article discusses the CAAPsnUseCase1 use case. This use case explains how to import a file based assembly in the ENOVIA VPM V4 database in Structure Exposed mode. The import is performed in batch from Windows platform. This use case makes reference to the CAAPsnUECreate use case which explains how implement the CATIPDMUECreate user exit required to set the attributes for the parts and documents that will be created in ENOVIA vpm V4. It also contains an implementation of the CATIPDMUECreate and CATIPDMUnixNTMapping interfaces that are not explained in detail in this use case. |
This use case is an example of how to use the SetPDMProperties method.
[Top]
CAAPsnUseCase1 is a use case of the CAAPSNInteroperability.edu framework that illustrates the PSNInteroperability framework capabilities.
[Top]
The goal of CAAPsnUseCase1 is to import in ENOVIA VPM V4 a file based assembly in Structure Exploded mode:
 |
 |
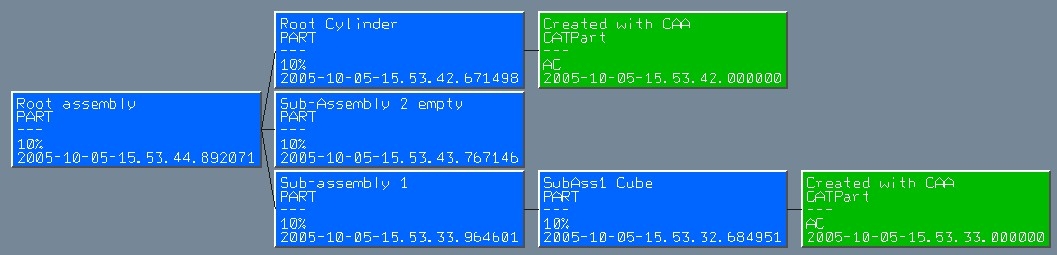
As a result of the execution of the use case, the following product structure is created in ENOVIA vpm V4
 |
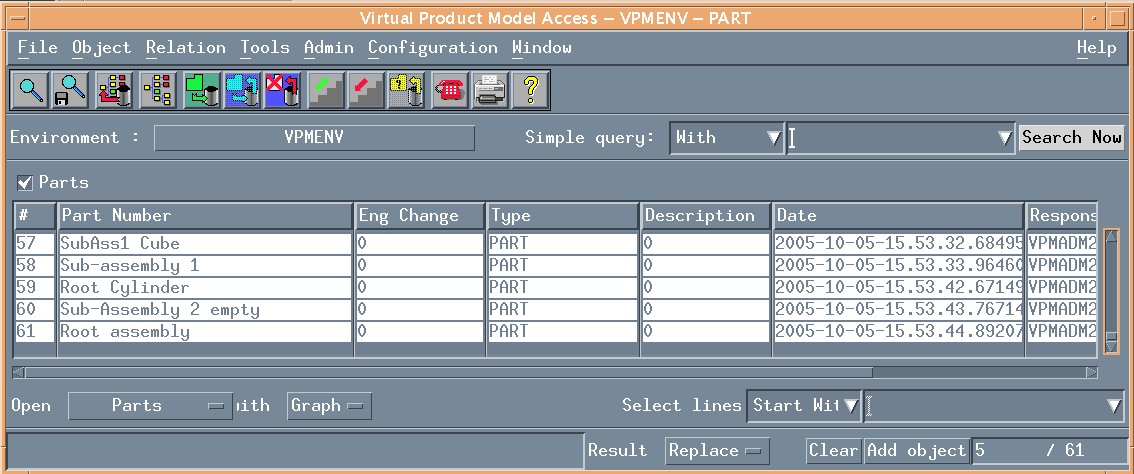
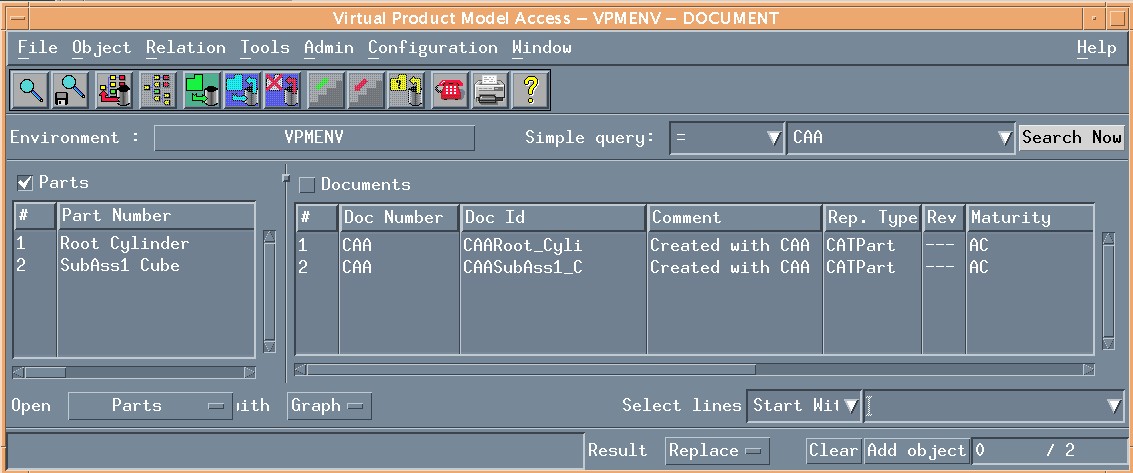
NoteRunning this use case creates new data in ENOVIA vpm V4. Prior to running it, we advise you to check if similar part number already exist in ENOVIA vpm as shown in the following panels:
 |
 |
[Top]
To launch CAAPsnUseCase1, you will need to set up the build time environment, then compile CAAPsnUseCase1 along with its prerequisites, set up the run time environment, and then execute the use case [1]. To launch it, execute the following command:
mkrun -c "CAAPsnUseCase1 rootFilepath hostName user pwd role server "
where
rootFilepath is the full path of the root document of the assembly.
This must be a CATProduct. All the documents referenced in this assembly are located
in the same directory.hostName is the name of the Unix host on which the communication
server will be launched.user is the user name used for the database connection.pwd is the password used for the database connection.role is the ENOVIA vpm role used to access the database.server is the name of the server in the option settings.[Top]
CAAPsnUseCase1 code is located in the CAAPsnUseCase1.m use case module of the CAAPSNInteroperability.edu framework:
| Windows | InstallRootDirectory/CAAPSNInteroperability.edu/CAAPsnUseCase1.m |
| Unix | InstallRootDirectory\CAAPSNInteroperability.edu\CAAPsnUseCase1.m |
where InstallRoot is the root directory of your CAA V5
installation. It is made of a unique source file named CAAPsnUseCase1.cpp.
[Top]
There are eight logical steps in CAAPsnUseCase1:
We will now comment each of those sections by looking at the code.
[Top]
CATUnicodeString rootFilepath = argv[1] ;
CATUnicodeString hostName = argv[2] ;
char * pHostName = argv[2] ;
CATUnicodeString user = argv[3] ;
CATUnicodeString pwd = argv[4] ;
CATUnicodeString role = argv[5] ;
CATUnicodeString server = argv[6] ;
|
CAAPsnUseCase1 begins by retrieving the arguments from the command line. Arguments are extracted in sequence: the full path of the root assembly document, the name of the Unix host, the ENOVIA vpm user and password used for database authentication, the role of this user and the option settings server name.
char* pCAAPathToShell=NULL;
CATLibStatus result = ::CATGetEnvValue("CV5VpmStart", &pCAAPathToShell);
if ( (CATLibError == result) || ( NULL == pCAAPathToShell) )
{
cout << "CV5VpmStart environment variable is not set" << endl << flush;
return 1;
}
cout << " The unix shell script is " << pCAAPathToShell << " on host " << hostName.ConvertToChar() << endl;
|
Then the CV5VpmStart environment variable is checked. It contains the name of the Unix
directory where the StartVPMBatchFromV5Batch.sh shell script is located.
char *sessionName = "CAA2_Sample_Session";
CATSession *pSession = NULL;
HRESULT rc = ::Create_Session(sessionName,
pSession);
if ((FAILED(rc)) || (NULL == pSession))
{
cout << "ERROR in creating session" << endl << flush;
return 1;
}
|
Since this is a batch program, it is first necessary to open a new
session before beginning to work with documents. Do not forget that this
session needs to be deleted at the end of the program.
To open a new session, use the Create_Session
global function.
[Top]
rc = ::CATInitBatchOnHost( pHostName );
if (SUCCEEDED(rc)) cout << "Communication with ENOVIA vpm is set" << endl << flush;
else
{
cout << "ERROR establishing communication with ENOVIA vpm" << endl << flush;
//Always deleting session before exiting
::Delete_Session(pSessionName);
return 1;
}
|
Now that the session is opened, you can establish the communication channel with ENOVIA vpm using
the CATInitBatchOnHost global method. This method establishes the connection with ENOVIA VPM V4
running on indicated Unix host.
If there is no server running to which the application can connect to,
a new ENOVIA VPM V4 server is launched on the dedicated Unix host.
[Top]
rc = ::CATConnectToVPM(server, user, pwd, role );
if (FAILED(rc))
{
cout << "ERROR in server authentication" << endl << flush;
//Always deleting session before exiting
::Delete_Session(pSessionName);
return 1;
}
|
Now that the connection to ENOVIA vpm is established, you can connect to the database
using the CATConnectToVPM global method. This method establishes the database connection
using user and password for authentication.
[Top]
CATDocument *pDocRoot = NULL;
rc = CATDocumentServices::OpenDocument( rootFilepath.ConvertToChar(), pDocRoot);
if (SUCCEEDED(rc) && (NULL != pDocRoot))
{
cout << "Document opened successfully" << endl << flush;
}
else
{
cout << "ERROR in opening the root document" << endl << flush;
//Always deleting session before exiting
::Delete_Session(pSessionName);
return 1;
}
|
Now that the session is opened, you can load the root assembly document using
the OpenDocument static method of CATDocumentServices.
This method requires, as a first parameter, the entire
storage path name and document name of the existing document that we want
to load into the session. In this use case, we enter this information as an
argument to the program. The second parameter of the Open
method returns a CATDocument pointer to the document it has loaded.
We assume that the pointed documents are loaded in session too. Thanks to the "Load Reference documents" options setting.
[Top]
const CATLISTP(CATDocument)* DocList = ::ListDocuments();
if (DocList)
{
for (int k=1; k<=DocList->Size(); k++)
{
CATDocument* pDocument = (*DocList)[k];
if ( NULL != pDocument )
{
CATIDocId * pIDocId = NULL ;
rc = pDocument->GetDocId(&pIDocId);
if ( SUCCEEDED(rc) )
{
CATUnicodeString type ;
pIDocId->GetType(type) ;
if ( CATUnicodeString("CATProduct") == type ) {
rc = CATVPMServices::SetPDMProperties( pDocument, CATVPMServices::VPM1, CATVPMServices::VolatileExposed );
}
else if ( CATUnicodeString("CATPart") == type ) {
rc = CATVPMServices::SetPDMProperties( pDocument, CATVPMServices::VPM1, CATVPMServices::PermanentBlackBox );
}
pIDocId->Release(); pIDocId = NULL;
}
if (FAILED(rc))
{
cout << "ERROR in setting PDM properties" << endl << flush;
return 1;
}
}
}
}
|
The CATProduct documents are stored in Structure Exploded mode while CATPart are stored in Publication Exposed mode.
You use the SetPDMProperties static method of CATVPMServices to set the right PDM property for each type of documents.
[Top]
CATBoolean UnloadAfterSave = FALSE;
rc = ::CATSaveInVPMFromCATIA( pDocRoot, UnloadAfterSave );
if (FAILED(rc))
{
cout << "ERROR in Saving documents in Enovia vpm" << endl << flush;
}
rc = ::CATCommitVPM();
|
You use the CATSaveInVPMFromCATIA global method to save the root product structure document.
The pointed documents are saved too.
You use the CATCommitVPM global method to commit the Save transaction in ENOVIA vpm.
[Top]
rc = ::CATDisconnectFromVPM(); |
You use the CATDisconnectFromVPM global method to disconnect from ENOVIA VPM V4 .
rc = ::CATTerminateBatch(); |
You use the CATTerminateBatch global method to terminate the V5 session.
[Top]
rc = ::Delete_Session(sessionName); |
Do not forget to delete the session at the end of the program using the Delete_Session
global function!
[Top]
This use case has demonstrated how to use the SetPDMProperties method for saving an assembly in Structure Exploded mode.
[Top]
| [1] | Building and Launching a CAA V5 Use Case |
| [Top] | |
| Version: 1 [Oct 2005] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2003, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.