You will find here information about the 1D property section type (also available with the local 1D properties).
-
Make sure a material was applied to the geometry and a linear 1D mesh part was assigned to the beam (it is already done in this particular case).
To know more about linear 1D mesh part, refer to Creating 1D Mesh Parts in this guide. -
You cannot apply 1D properties and 1D mesh parts on geometry included in a sketch.
Open the sample52.CATAnalysis document from the sample directory.
You can select different section types.
For each Type option, you have to click the Component
Edition icon
![]() in the 1D Property dialog box to define the parameters of the section.
in the 1D Property dialog box to define the parameters of the section.
Type: lets you
choose the type of section (and symbol) and define the parameters.
|
Cylindrical beam: |
|
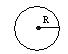 |
|
Tubular beam: |
|
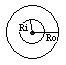 |
|
Rectangular beam: |
|
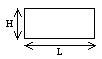 |
|
Thin Box beam: |
|
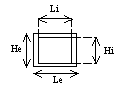 |
|
Thin U-beam: |
|
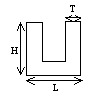 |
|
Thin I-beam: |
|
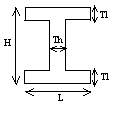 |
|
Thin T-beam: |
|
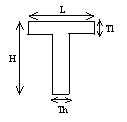 |
|
Thin X-beam: |
|
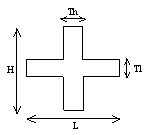 |
|
User-defined beam: |
|
Any section |
|
|
|
Any surface section* |
|
|
|
Any section which works in traction/strain* |
|
|
|
Any section at each extremities |
Where :
- Ixx, Iyy and Izz are the three
components of the inertia matrix of the beam, expressed in the principal
axis of the beam (axis in which the matrix is diagonal):
- Ixx is the torsion coefficient.
- Iyy is the area moment of inertia in the XZ-plane.
- Izz is the area moment of inertia in the XY-plane.
- Shear center (Y) is the y-coordinate of the shear center in the section axis, centered at the center of gravity of the section.
- Shear center (Z) is the z-coordinate of the shear center in the section axis, centered at the center of gravity of the section.
- Shear Factor (XY) is the ratio between the
cross-sectional area (A) and the shear area (Ay),
area section which works in shearing in the XY-plane (case of
a short beam).
Shear Factor (XY) = A / Ay
This ratio should be greater than one. - Shear Factor (XZ): is the ratio between the
cross-sectional area (A) and the shear area (Az),
area section which works in shearing in the XZ-plane (case of
a short beam).
Shear Factor (XZ) = A / Az
This ratio should be greater than one.
|
|
*:
|