3D PLM PPR Hub Open Gateway |
Knowledge Modeler |
About UnitsSome Tips about the Units Managed in Literal Applications |
| Technical Article | ||
AbstractThis article focuses on the subtleties about using units in CATIA.
|
[Top]
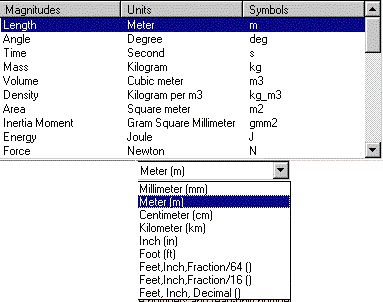
The end user view of units is entirely managed by the Tools->Options->Units settings.

The units selected by the end-user are those displayed in the ![]() dialog box when you create a parameter. For example, if the meter (m) has been
selected for the unit of the Length type magnitude, the unit displayed in the
value field when you create a new parameter of Length type will be the meter.
Likewise, the parameter values in the specification tree as well as the values
displayed in the feature editors will be displayed in meters.
dialog box when you create a parameter. For example, if the meter (m) has been
selected for the unit of the Length type magnitude, the unit displayed in the
value field when you create a new parameter of Length type will be the meter.
Likewise, the parameter values in the specification tree as well as the values
displayed in the feature editors will be displayed in meters.
When you run a CATIA session and modify your settings, you override the default setting files. This new settings are stored in your environment as 'profiles' and reused when you reopen a CATIA session or execute a batch sample.
[Top]
There are a number of methods whereby you can modify or access literal values. Here is a description of these methods as well as the units they support or return.
[Top]
Literals are created by using the CATICkeParmFactory::Createxxx
methods. The value passed as the argument of a creation method should always be
specified in the MKS Unit System (MKS stands for meters, kilograms, seconds).
Examples:
// The initial value of "Radius" is 2.5 meters
CATICkeParm_var
spRadius = spFact->CreateLength ("Radius",2.5);
// The initial value of "vol" is 2 cubic meters
CATICkeParm_var
spVolume = spFact->CreateDimension (CATParmDictionary::FindMagnitude("VOLUME"),"vol",2);
|
[Top]
Literal values are modified by using the CATICkeInst::Valuate method. The value passed as the argument should always be specified in the MKS unit system.
Examples:
// The new value of "Radius" is 4 meters spRadius->Valuate(4); // The new value of "vol" is 50 cubic meters spVolume->Valuate(50); |
[Top]
Literal values are retrieved by using the CATICkeInst::AsReal or AsType methods. These methods return the parameter value in MKS units.
Examples:
// Display 4 (meters) cout << spRadius->Value()->AsReal(); // Display 50 (cubic meters) cout << spVolume->Value()->AsReal(); |
[Top]
Literal values are displayed by using the CATICkeParm::Show method which displays a value with the units specified in your CATIA settings (Tools->Options->Units).
Examples:
// Display 4000mm if the Length default unit specified in the settings is the mm cout << spRadius->Show().CastToCharPtr(); // Display 50 (cubic meters) if the Volume default unit specified in the settings is the m3 cout << spVolume->Show().CastToCharPtr(); |
[Top]
The stored value of a parameter is retrieved by using the CATIParmAsStored::ValueStored method which returns the value in internal units. The internal units are the units the geometric modeler uses when performing internal computations. You can't change these units. The internal unit for a Length is the mm. The internal unit for an angle is the degree.
Examples:
// Display 4000mm CATIParmAsStored_var spStoredRadius = spRadius; cout << spStoredRadius->ValueStored() << endl; |
[Top]
Use the following methods to manage units and magnitudes.
CATICkeParmFactory::Createxxx |
To create a parameter and set its initial value in MKS units. |
CATICkeParm::Valuate |
To assign a value in MKS units. |
CATICkeInst::AsReal, AsType |
To retrieve a value in MKS units. |
CATICkeParm::Show |
To display a value in the CATIA setting units. |
CATICkeParm::ValueStored |
To retrieve a value in internal units. |
[Top]
| Version: 1 [Jan 2000] | Document created |
| [Top] | |
Copyright © 2000, Dassault Systèmes. All rights reserved.