This task shows how to create a Rigid Virtual Part between a point and a geometry support.
A Rigid Virtual Part is a rigid body connecting a specified point to specified part geometries, behaving as a mass-less rigid object which will stiffly transmit actions (masses, restraints and loads) applied at the handle point, while locally stiffening the deformable body or bodies to which it is attached.
The Rigid Virtual Part does not take into account the elastic deformability of the parts to which it is attached.
The program proceeds as follows:
- a node is created in coincidence with the specified handle point.
- each node of the specified geometry supports meshes is connected by a kinematical rig-beam element to the handle node.
- a set of rig-beam relations is generated between the handle node degree of freedom and the connected nodes degree of freedom.
Thus, the Rigid Virtual Part generates as many rig-beam
kinematical elements as there are nodes on specified support meshes.
The Rigid Virtual Part is built with a Rigid Spider element.
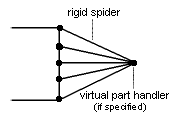
To know more about this element, refer to Rigid Spider in the Finite Element Reference Guide.
Rigid Virtual Parts can be applied to the following types of supports:
|
Geometrical Feature |
Mechanical Feature |
Analysis Feature |
||||
|
Spatial Groups |
Geometrical Groups |
Groups by Neighborhood |
Groups by Boundary |
Others |
||
|
Edge |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Open the
sample28.CATAnalysis document from the samples directory.
A Part Design point was created in the pointed .CATPart document.
-
Go to View > Render Style > Customize View and make sure the Shading, Outlines and Materials options are active in the Custom View Modes dialog box.
-
Click Rigid Virtual Part
 in the Virtual Parts toolbar.
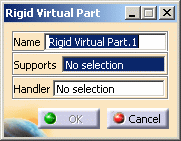
in the Virtual Parts toolbar.The Rigid Virtual Part dialog box appears.
-
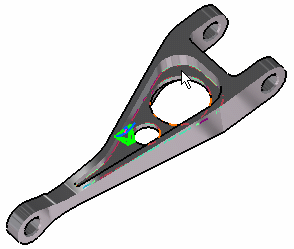
Select a face or an edge of the part as a geometry support. In this particular case, select a face.
-
Position the cursor on the Handler field in the Rigid Virtual Part dialog box and select a vertex or a point as handler point (the handler point symbol appears as your cursor passes over it). In this case, select a point.
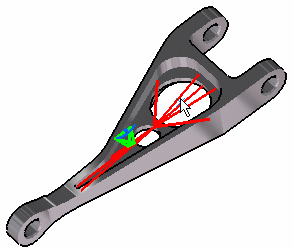

- This point selected as handler must be a Part Design point.
- If you do not specifically select a point, the centroid (the point at which the lines meet) will be used as the handler point.
- When several virtual parts share a same handler point, only one finite element node is generated.
The Rigid Virtual Part dialog box is updated.
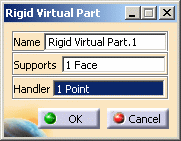
-
Click OK.
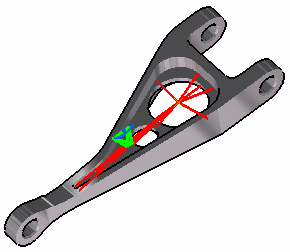
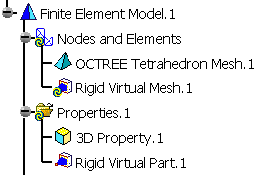
Both Rigid Virtual Part.1 and Rigid Virtual Mesh.1 appear in the specification tree.
When a 1D mesh part is created by selecting two virtual parts handler, the nodes are not condensed. The beam mesh part must be created first.
Do not use virtual parts to simulate connections. You should use the Analysis Connection.
-
You can select several geometry supports.
-
The Rigid Virtual Part will connect all supports to the handle point and stiffly transmit all actions as a rigid body.
![]()