This task shows you how to create an Acceleration applied to a part.
Accelerations are intensive loads representing mass body
force (acceleration) fields of uniform magnitude applied to parts.
Units are mass body force (or acceleration) units (typically N/kg,
or m/s2 in SI).
Acceleration objects belong to Loads objects sets.
You need to specify three components for the direction of the field, along with a magnitude information. Upon modification of any of these four values, the mass body force vector components and magnitude are updated based on the last data entry.
Accelerations can be applied to the following types of supports:
|
Geometrical Feature |
Mechanical Feature |
Analysis Feature |
||||
|
Spatial Groups |
Geometrical Groups |
Groups by Neighborhood |
Groups by Boundary |
Others |
||
|
Body 1D |
|
|
|
|
|
Mesh Part |
* To simulate the application of a weight on a virtual part, you must apply a mass and then an acceleration on this virtual part.
To know more, refer to Authorized Supports.
Open the sample00.CATAnalysis document from the samples directory.
-
Go to View > Render Style > Customize View and make sure the Shading, Outlines and Materials options are active in the Custom View Modes dialog box.
-
Click Acceleration
 in the Loads toolbar.
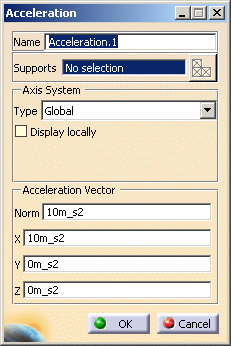
in the Loads toolbar.The Acceleration dialog box appears.
-
You can change the identifier of the Acceleration by editing the Name field.
-
Set the Axis System.
The Axis System Type combo box allows you to choose between Global and User Axis systems for entering components of the acceleration field.
- Global: if you select the Global Axis system, the components of the acceleration field will be interpreted as relative to the fixed global rectangular coordinate system.
- User: if you select a User Axis
system, the components of the acceleration field will be
interpreted as relative to the specified rectangular coordinate
system.
To select a User Axis system, you must activate an existing Axis by clicking it in the specification tree. Its name will then be automatically displayed in the Current Axis field.

- You can define the mass body force direction by using the compass.
- You can modify the compass orientation either with the mouse or by editing the compass.
- By applying the compass to any part geometry, you can align the compass directions with the implicit axis directions of that geometry: drag the compass by handling the red square and drop it on the appropriate surface. The normal direction to this surface defines the new direction. Then, click on the Compass Direction button to take this new direction into account. You can now invert the direction if desired, editing the values of the three components.
-
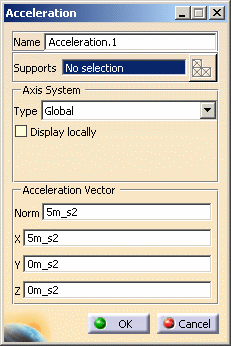
Enter values for the X, Y, Z components of the mass body force field: the corresponding Norm value is automatically computed and displayed.
-
Select the geometry support (a part) on which the mass body force is to be applied.
Any selectable geometry is highlighted when you pass the cursor over it.
You can select several supports in sequence, to apply the Acceleration to all supports simultaneously.
Symbols representing the Acceleration are displayed on the support geometry to visualize the volume body force field.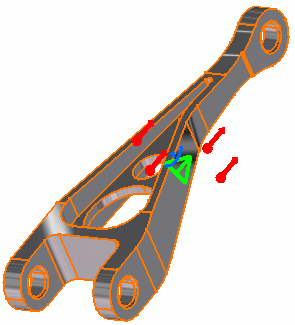
The remaining three fields are automatically computed and displayed. The visualized symbols orientation is also updated to reflect the modification.
As soon as the support is selected, the Select Mesh Part button is available.
To know more about the Select Mesh Part button, refer to Selecting Mesh Parts. -
Click OK.
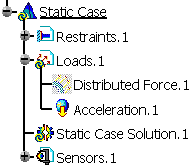
Acceleration.1 appears in the specification tree under the active Loads.1 set.
- You can either select the part and then set the Acceleration specifications, or set the Acceleration specifications and then select the part.
- If you select other parts, you can create as many Acceleration loads as desired with the same dialog box. A series of Accelerations can therefore be created quickly.
- Loads are required for Stress Analysis computations.
- If several Analysis Cases have been defined in the Finite Element Model, you must activate a Loads objects set in the specification tree before creating an Acceleration object (only available if you installed the ELFINI Structural Analysis product).
- Acceleration objects can be edited by a double click on the corresponding object or icon in the specification tree.
Make sure the computation is finished before starting any of the below operations.
Products Available in Analysis Workbench
The ELFINI Structural Analysis (EST) product offers the following additional features with a right-click:
-
 on an Acceleration object:
on an Acceleration object:
- Translational acceleration visualization on mesh: the translation of your Acceleration object specifications into solver specifications can be visualized symbolically at the impacted mesh elements, provided the mesh has been previously generated via a Compute action.
-
 on a Loads set:
on a Loads set:
- Generate Image: generates an image of the computed Load objects (along with translating all user-defined Loads specs into explicit solver commands on mesh entities), by generating symbols for the elementary loads imposed by the Loads objects set. The image can be edited to include part or all of the options available.
- Report: the partial status and results of intermediate
pre-processor computations are reported in HTML format. It represents a
subset of the global Report capability and generates a partial report
of the Loads objects set Computation.
Refer to Creating Pressures for more details. - Self-balancing: refer to Creating Pressures for more details.
![]()