The following section aims at describing silhouette operation in more
details:
How is the Silhouette Representation Calculated?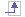
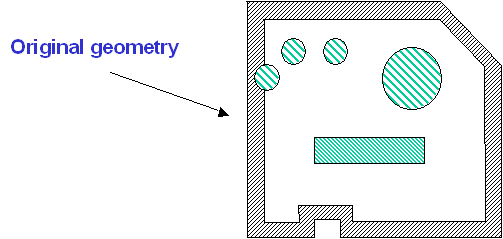
You obtain the silhouette of a specific geometry by:
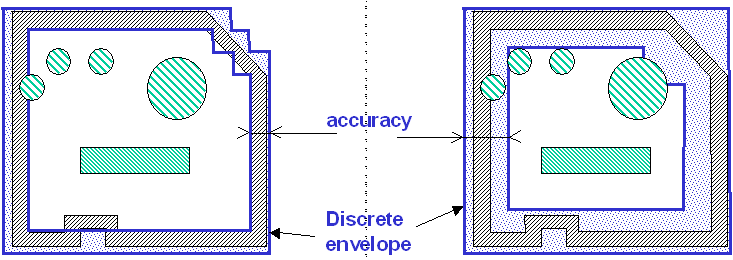
- calculating a discrete envelope of the initial representation (discretization
parameter = accuracy)
- filtering the triangles of the geometry which:
- do not belong to this envelope,
- are not seen from the selected view (s).
The following example aims at illustrating these two steps as well as
the impact of accuracy and view parameters on the final result.
Step 1: Calculating the Envelope Using
the Accuracy Parameter
Case 1: You select a small accuracy value
|
Case 2: You select great accuracy value
|
 |
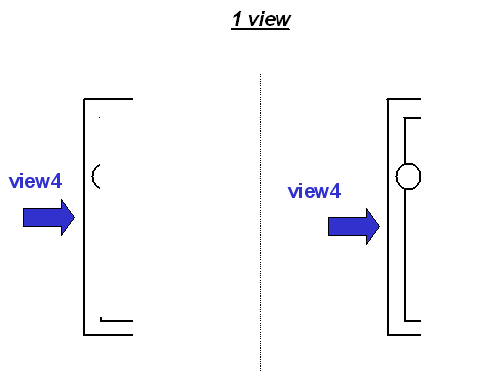
Step 2: Filtering Triangles Using the
View Parameter
Case 1: Result obtained when 4 views are selected
Case 2: Result obtained when 1 view is selected
How the Accuracy Parameter Impacts the
Silhouette Calculation ? ?
The table below shows the accuracy impact on the silhouette
calculation:
Accuracy
|
Computation Time
|
Used Memory
|
Simplification Rate
|
 Greater Greater |
 Shorter Shorter |
 Less Less |
 Lower Lower |
 Smaller Smaller |
 Longer Longer |
 More More |
 Higher Higher |
|




 ?
?